| Immunotherapy for Merkel Cell Carcinoma | ||||||
| Therapy | Study | Line of Therapy | N | Objective Response (%) | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avelumab | Javelin1 | 1 | 116 | 40 | 4.1 | 20.3 |
| Avelumab | Javelin2,3 | ≥2 | 88 | 33 | 3 | 12.6 |
| Pembrolizumab | CITN-094 | 1 | 50 | 58 | 16.8 | NR |
| Nivolumab | CheckMate-3585 | 1 | 15 | 73 | 24.8 | NR |
| Nivolumab | CheckMate-3585 | ≥2 | 10 | 50 | 21.3 | NR |
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | CheckMate-3581 | 1 | 33 | 64 | 15.4 | 35.58 |
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | Moffitt IST6 | 1 | 13 | 100 | NR | NR |
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | CheckMate-3581 | ≥2 | 10 | 40 | 2.74 | 8.56 |
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | Moffitt IST6 | ≥2 | 12 | 42 | 4.2 | 14.9 |
| Retifanlimab | POD1UM-2017 | 1 | 65 | 52 | NA | NA |
|
References: 1 Bhatia et al. (2023) 2 Kaufman et al. (2018) 3 Kaufman et al. (2016) 4 Nghiem et al. (2016) 5 Topalian et al. (2017) 6 Kim et al. (2022) 7 Grignani et al. (2021)
|
||||||
Should Ipilimumab Be the New “Standard” for Refractory MCC?
David M. Miller MD, PhD
MassGeneral Cancer Center
Harvard Medical School
Third International Merkel Cell Carcinoma Conference Houston, Texas 77030
Disclosures
I have received honoraria for participation on advisory boards for Merck, EMD Serono, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Pfizer, Castle Biosciences, Checkpoint Therapeutics, Incyte, Bristol-Myers Squib. I have stock options from Checkpoint Therapeutics and Avstera Therapeutics. I have received research funding from Regeneron, Kartos Therapeutics, Xilio Therapeutics, NeoImmune Tech, Inc, Project Data Sphere, ECOG-ACRIN and the American Skin Association.
Overview
- Background on the therapeutic landscape for MCC
- Review data on ipilimumab in the post-PD1 setting
- Provide concluding thoughts
Figure created using skincancerRx (https://github.com/TheMillerLab/skincancerRx)
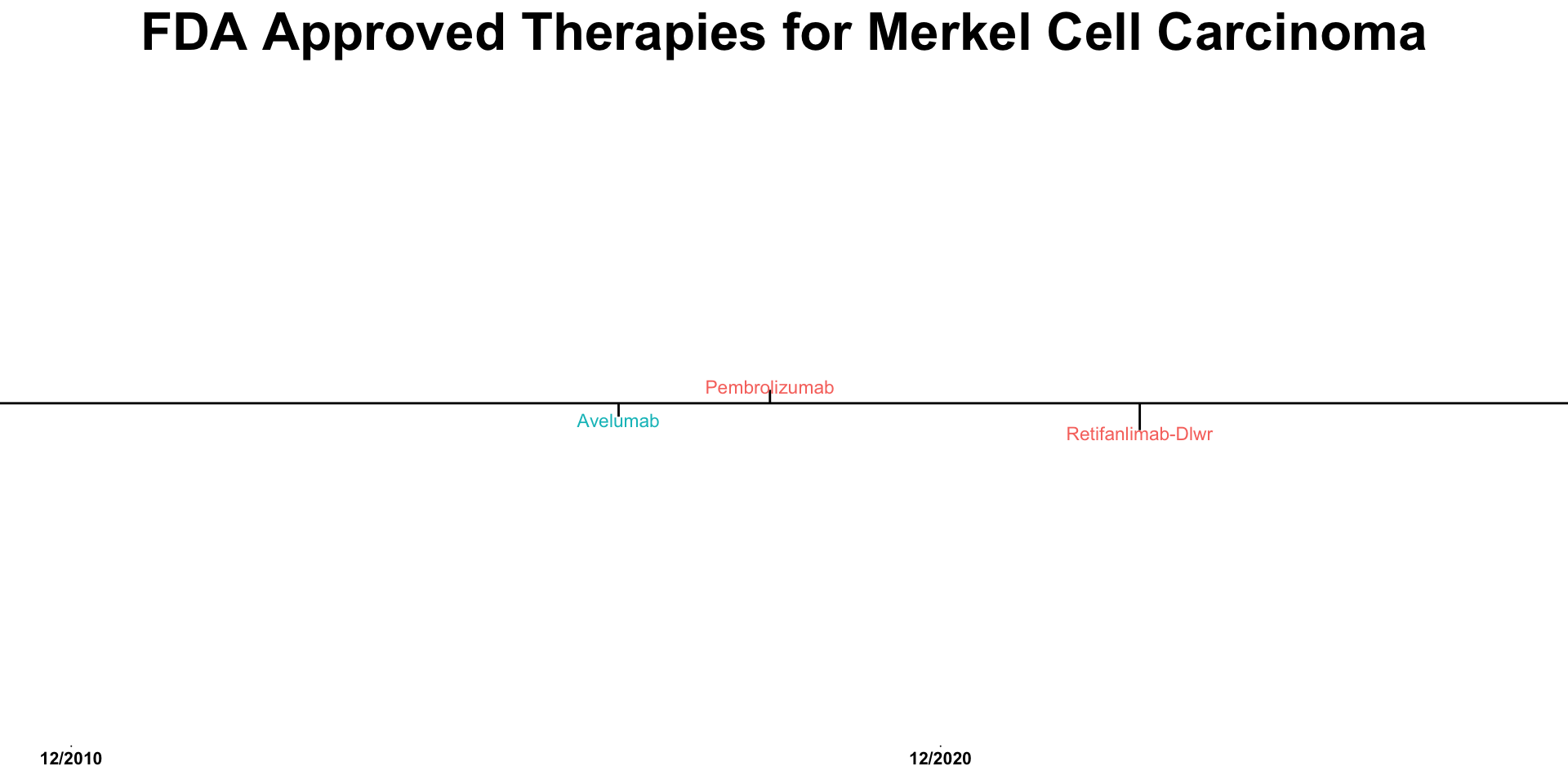
Figure created using skincancerRx (https://github.com/TheMillerLab/skincancerRx)
Table derived from Miller et al. (2023)
| Immunotherapy for Merkel Cell Carcinoma | ||||||
| Therapy | Study | Line of Therapy | N | Objective Response (%) | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avelumab | Javelin | 1 | 116 | 40 | 4.1 | 20.3 |
| Pembrolizumab | CITN-09 | 1 | 50 | 58 | 16.8 | NR |
| Nivolumab | CheckMate-358 | 1 | 15 | 73 | 24.8 | NR |
| Retifanlimab | POD1UM-201 | 1 | 65 | 52 | NA | NA |
Table derived from Miller et al. (2023)
| Immunotherapy for Merkel Cell Carcinoma | ||||||
| Therapy | Study | Line of Therapy | N | Objective Response (%) | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avelumab | Javelin | 1 | 116 | 40 | 4.1 | 20.3 |
| Pembrolizumab | CITN-09 | 1 | 50 | 58 | 16.8 | NR |
| Nivolumab | CheckMate-358 | 1 | 15 | 73 | 24.8 | NR |
| Retifanlimab | POD1UM-201 | 1 | 65 | 52 | NA | NA |
| Aggregate | Aggregate | 1 | 246 | 49 | NA | NA |
Table derived from Miller et al. (2023)
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
Unmet Need
- Therapies in the post-PD1 setting are lacking
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
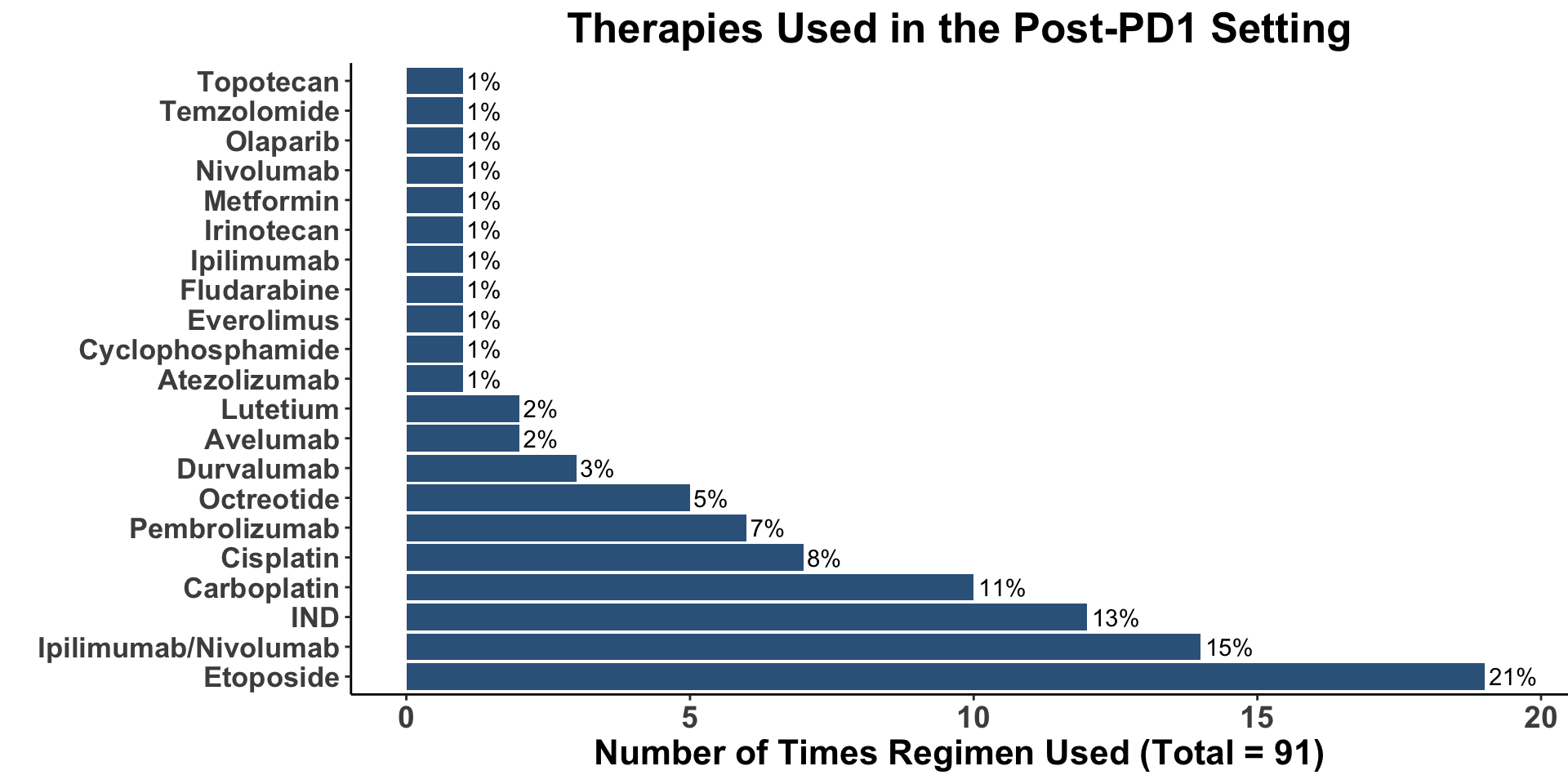
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
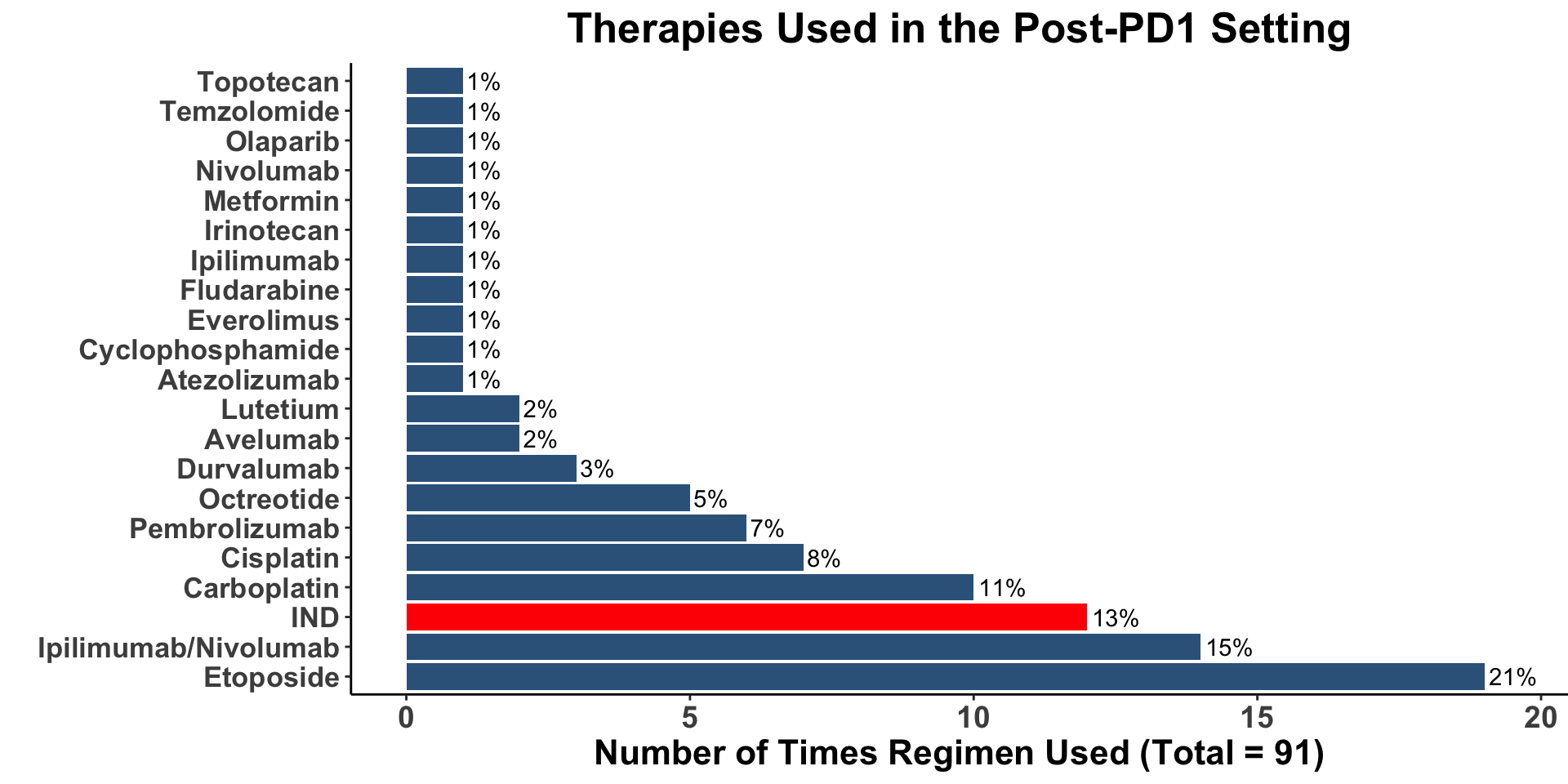
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
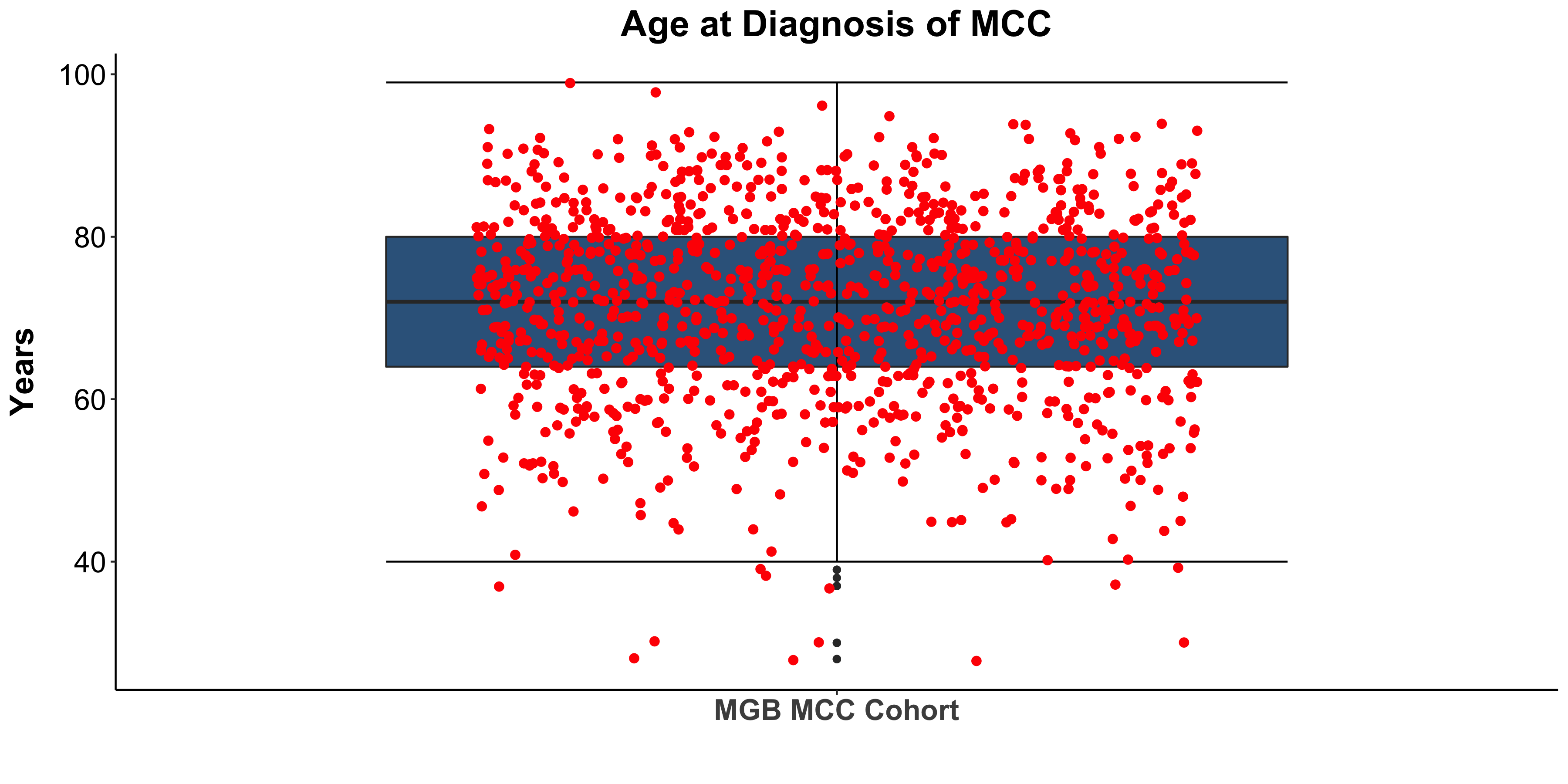
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
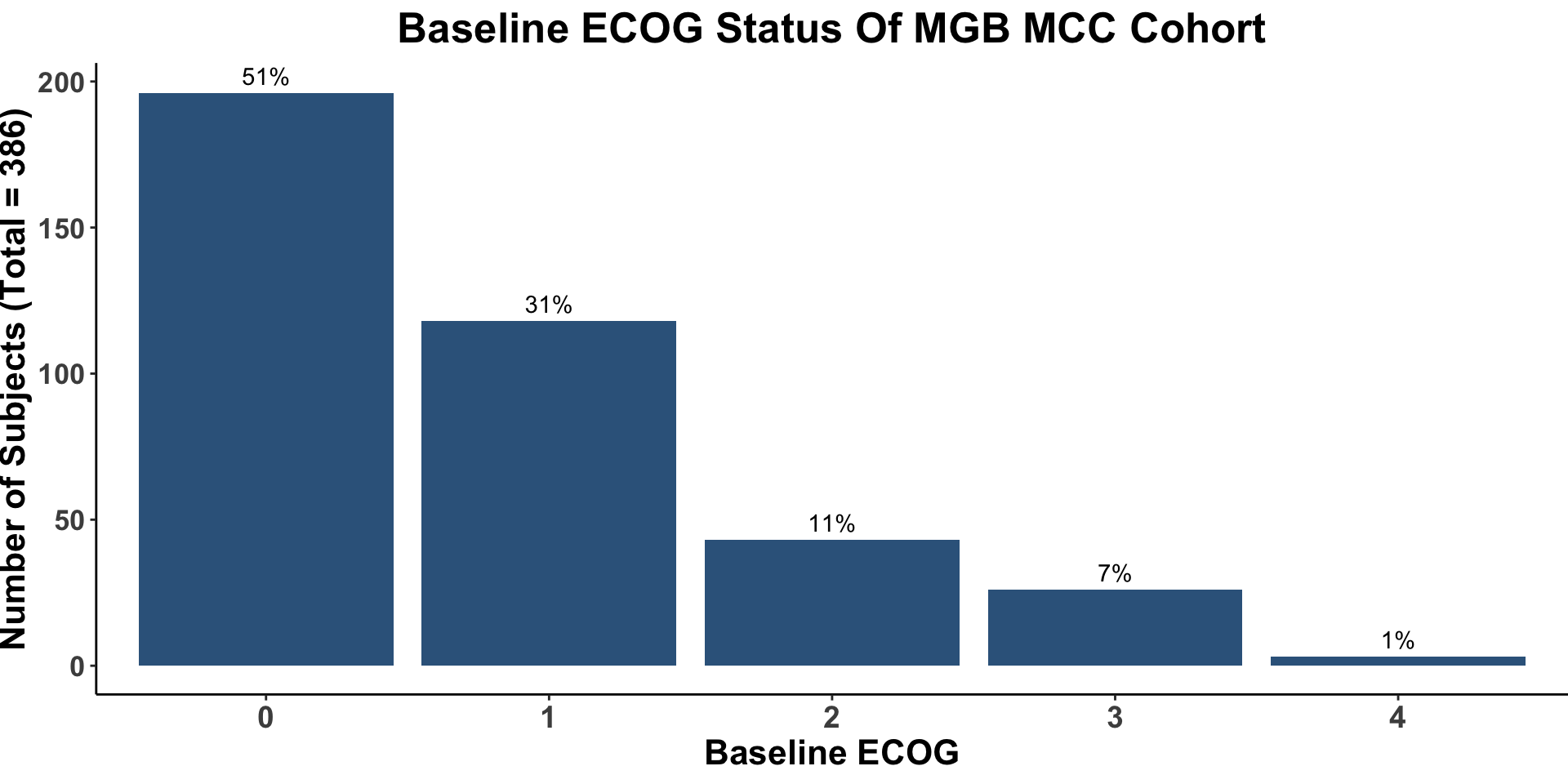
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
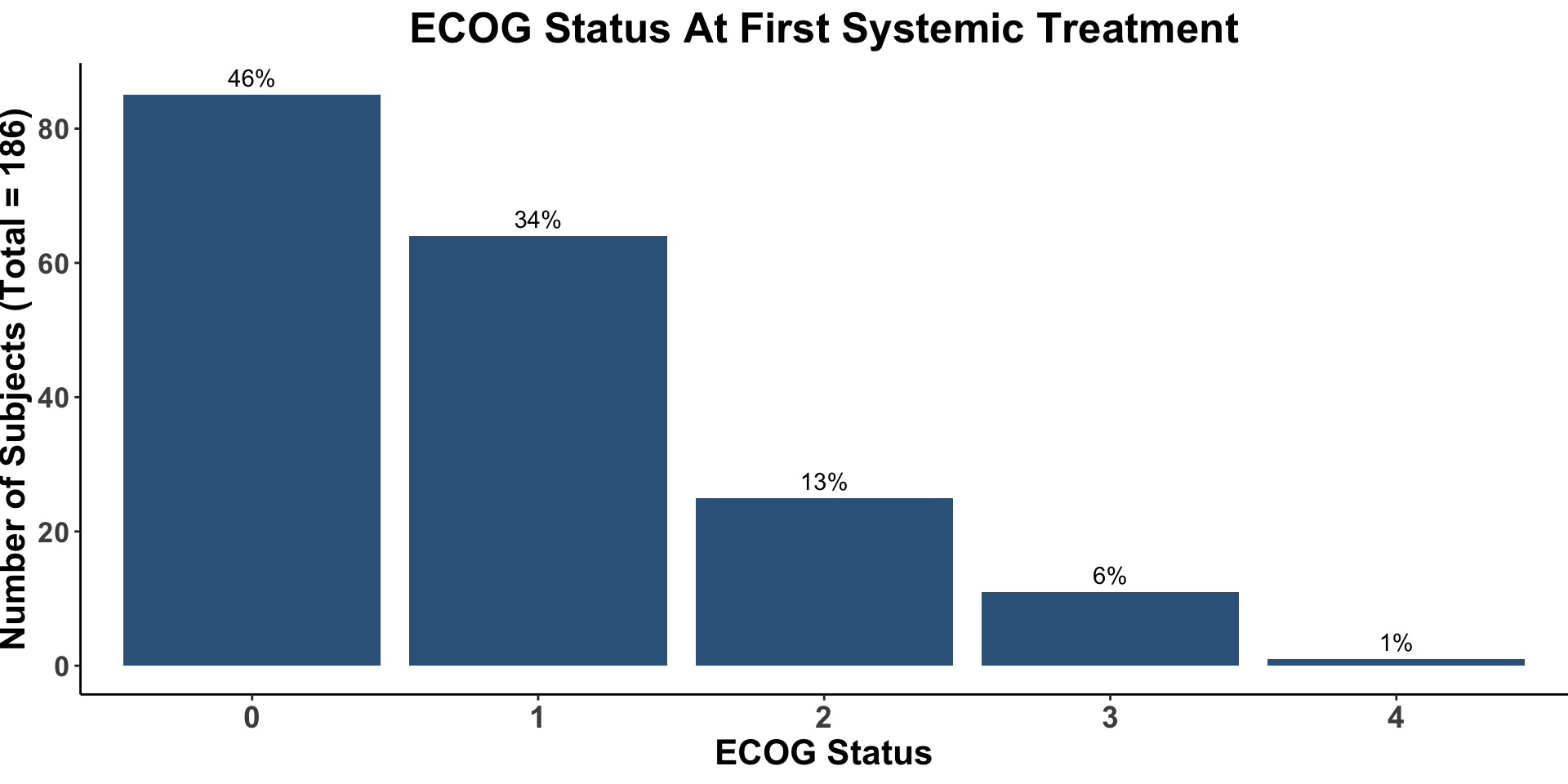
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
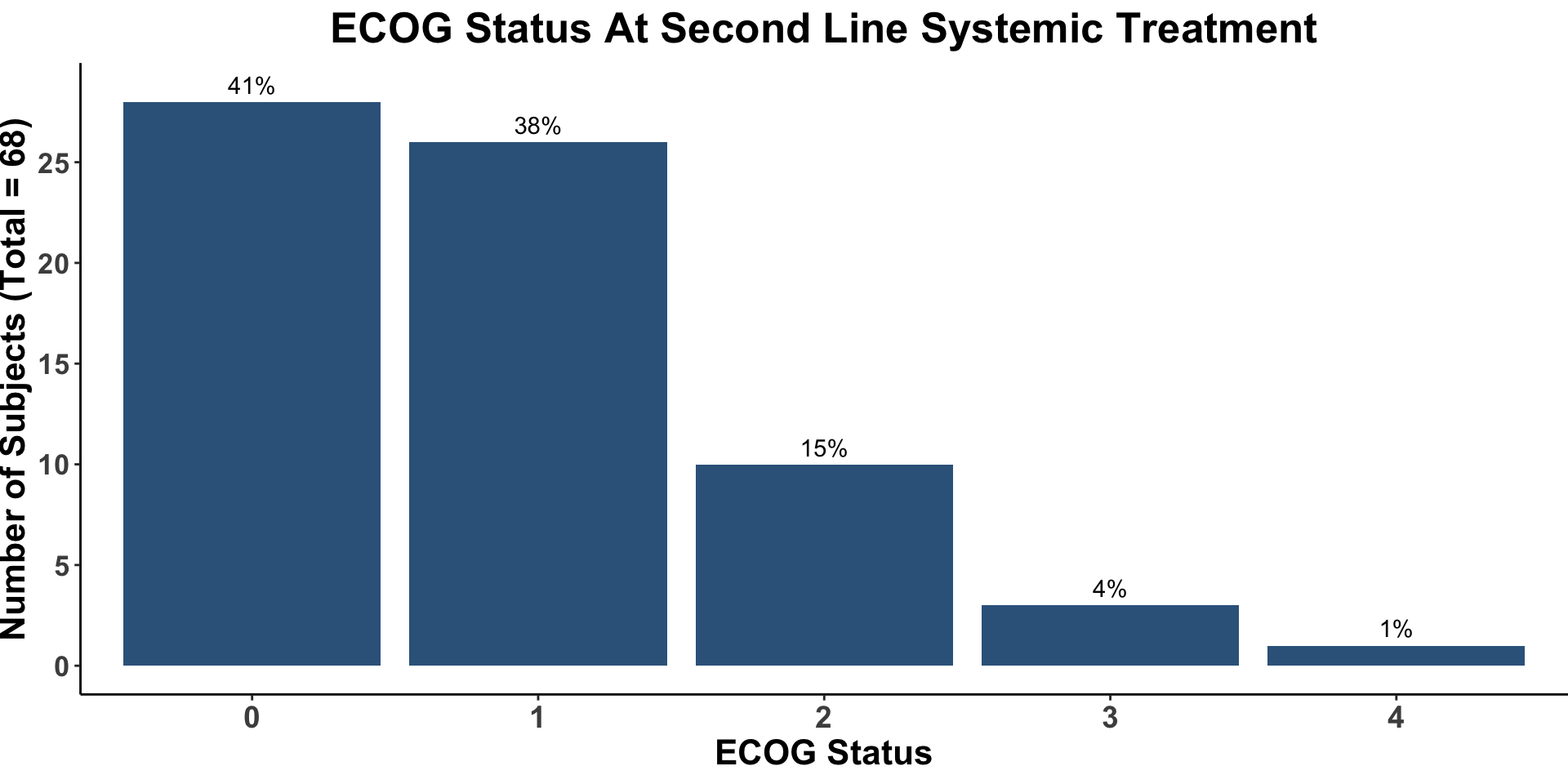
Miller, Kaufman, Emerick, Silk, Thakuria et al. Unpublished data from BWH/DFCI & MGH MCC Cohort
Rationale of anti-CTLA4
Rationale of anti-CTLA4
- CTLA-4 regulates T-cell activation in lymphoid tissue(Buchbinder and Desai 2016)
- Combination anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4 has a long history of efficacy and a known safety profile (Larkin et al. 2015)
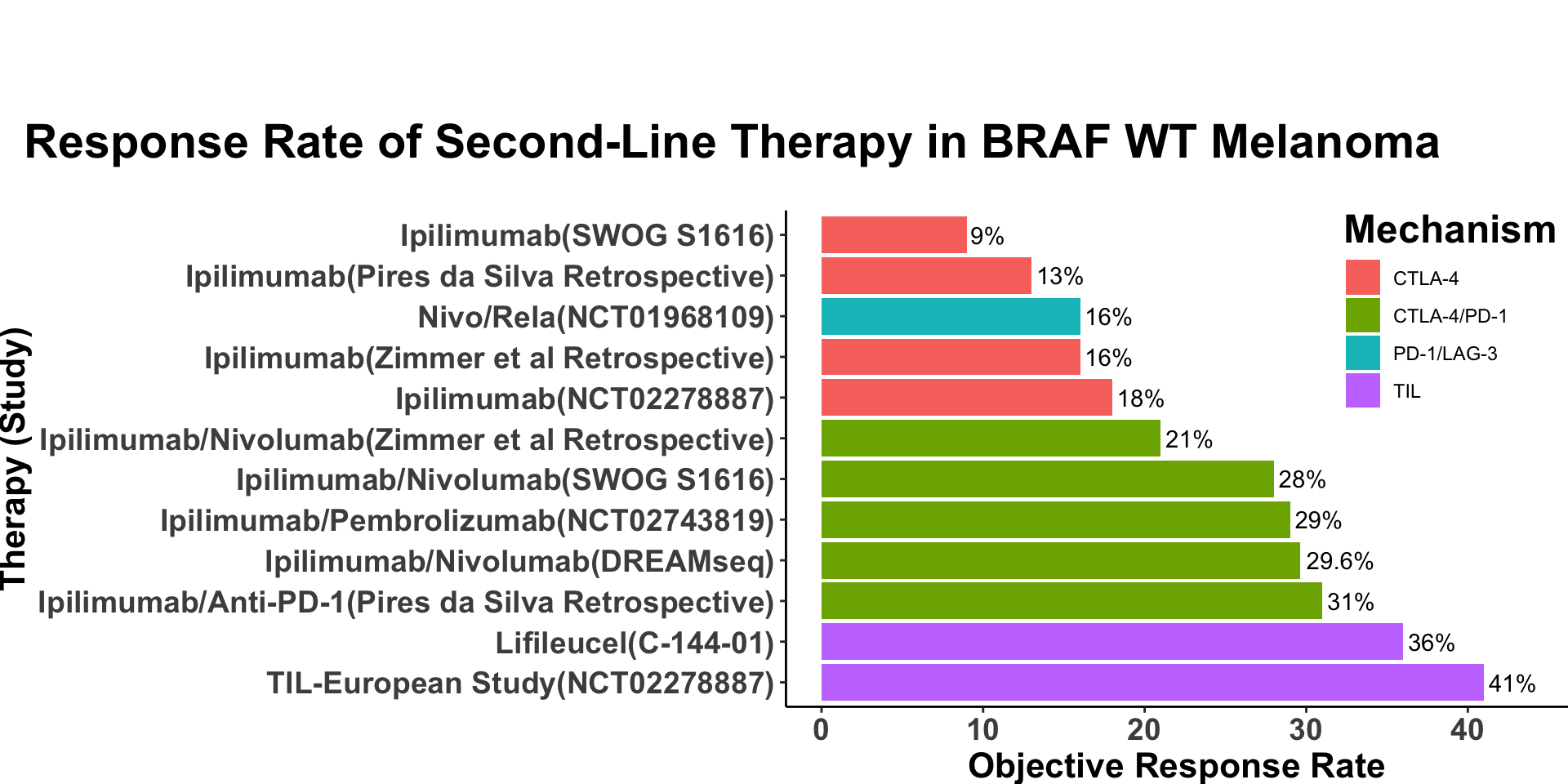
Targeting CTLA-4 in MCC
- Efficacy in the first line setting
| Ipilimumab As First Line Systemic Therapy | ||||||||||||
| Patient | Sex | Age at First Diagnosis (years) | First Diagnosis | Initial Tumor Localization | Therapies Before Ipilimumab | Start of Ipilimumab | Adjuvant/Additive | Number of Cycles | Best Response | PFS (months) | Therapies Following Ipilimumab | OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 55 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation | 03/14 | No | 4 | PD | 2.8 | None | 3.5 |
| 2 | M | 70 | 07/12 | Right thigh | Right inguinal/iliac/paracaval lymphadenectomy and radiation, radiation to left iliac lymph nodes | 01/14 | No | 4 | SD | 12.0 | Radiation to cervical lymph nodes, nivolumab, radiation to left paraaortal lymph node, etoposide | >36.2 |
| 3 | M | 81 | 12/10 | Right lower leg, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, excision right thigh and radiation | 01/12 | Additive (surgery) | 3 | SD | 4.8 | Radiation to right retroperitoneal lymph nodes, radiation to right renal bed | 15.8 |
| 4 | M | 61 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection, left iliac lymph node dissection, radiation to left pelvis, low-dose interferon, radiation to paraaortal lymph node | 08/14 | Adjuvant (radiation) | 4 | CR | 12.6 | Radiation to paraaortal lymphatic pathways, ipilimumab | >28.6 |
| 5 | F | 50 | 02/11 | Left knee, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymphadenectomy, radiation to the knee and right inguinal | 01/15 | Additive (radiation) | 4 | CR | 23.5 | None | >23.5 |
Table derived from Winkler et al. (2017)
| Ipilimumab As First Line Systemic Therapy | ||||||||||||
| Patient | Sex | Age at First Diagnosis (years) | First Diagnosis | Initial Tumor Localization | Therapies Before Ipilimumab | Start of Ipilimumab | Adjuvant/Additive | Number of Cycles | Best Response | PFS (months) | Therapies Following Ipilimumab | OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 55 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation | 03/14 | No | 4 | PD | 2.8 | None | 3.5 |
| 2 | M | 70 | 07/12 | Right thigh | Right inguinal/iliac/paracaval lymphadenectomy and radiation, radiation to left iliac lymph nodes | 01/14 | No | 4 | SD | 12.0 | Radiation to cervical lymph nodes, nivolumab, radiation to left paraaortal lymph node, etoposide | >36.2 |
| 3 | M | 81 | 12/10 | Right lower leg, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, excision right thigh and radiation | 01/12 | Additive (surgery) | 3 | SD | 4.8 | Radiation to right retroperitoneal lymph nodes, radiation to right renal bed | 15.8 |
| 4 | M | 61 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection, left iliac lymph node dissection, radiation to left pelvis, low-dose interferon, radiation to paraaortal lymph node | 08/14 | Adjuvant (radiation) | 4 | CR | 12.6 | Radiation to paraaortal lymphatic pathways, ipilimumab | >28.6 |
| 5 | F | 50 | 02/11 | Left knee, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymphadenectomy, radiation to the knee and right inguinal | 01/15 | Additive (radiation) | 4 | CR | 23.5 | None | >23.5 |
Table derived from Winkler et al. (2017)
| Ipilimumab As First Line Systemic Therapy | ||||||||||||
| Patient | Sex | Age at First Diagnosis (years) | First Diagnosis | Initial Tumor Localization | Therapies Before Ipilimumab | Start of Ipilimumab | Adjuvant/Additive | Number of Cycles | Best Response | PFS (months) | Therapies Following Ipilimumab | OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 55 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation | 03/14 | No | 4 | PD | 2.8 | None | 3.5 |
| 2 | M | 70 | 07/12 | Right thigh | Right inguinal/iliac/paracaval lymphadenectomy and radiation, radiation to left iliac lymph nodes | 01/14 | No | 4 | SD | 12.0 | Radiation to cervical lymph nodes, nivolumab, radiation to left paraaortal lymph node, etoposide | >36.2 |
| 3 | M | 81 | 12/10 | Right lower leg, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, excision right thigh and radiation | 01/12 | Additive (surgery) | 3 | SD | 4.8 | Radiation to right retroperitoneal lymph nodes, radiation to right renal bed | 15.8 |
| 4 | M | 61 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection, left iliac lymph node dissection, radiation to left pelvis, low-dose interferon, radiation to paraaortal lymph node | 08/14 | Adjuvant (radiation) | 4 | CR | 12.6 | Radiation to paraaortal lymphatic pathways, ipilimumab | >28.6 |
| 5 | F | 50 | 02/11 | Left knee, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymphadenectomy, radiation to the knee and right inguinal | 01/15 | Additive (radiation) | 4 | CR | 23.5 | None | >23.5 |
Table derived from Winkler et al. (2017)
| Ipilimumab As First Line Systemic Therapy | ||||||||||||
| Patient | Sex | Age at First Diagnosis (years) | First Diagnosis | Initial Tumor Localization | Therapies Before Ipilimumab | Start of Ipilimumab | Adjuvant/Additive | Number of Cycles | Best Response | PFS (months) | Therapies Following Ipilimumab | OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 55 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation | 03/14 | No | 4 | PD | 2.8 | None | 3.5 |
| 2 | M | 70 | 07/12 | Right thigh | Right inguinal/iliac/paracaval lymphadenectomy and radiation, radiation to left iliac lymph nodes | 01/14 | No | 4 | SD | 12.0 | Radiation to cervical lymph nodes, nivolumab, radiation to left paraaortal lymph node, etoposide | >36.2 |
| 3 | M | 81 | 12/10 | Right lower leg, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymph node dissection and radiation, excision right thigh and radiation | 01/12 | Additive (surgery) | 3 | SD | 4.8 | Radiation to right retroperitoneal lymph nodes, radiation to right renal bed | 15.8 |
| 4 | M | 61 | 07/13 | Left inguinal lymph nodes | Left inguinal lymph node dissection, left iliac lymph node dissection, radiation to left pelvis, low-dose interferon, radiation to paraaortal lymph node | 08/14 | Adjuvant (radiation) | 4 | CR | 12.6 | Radiation to paraaortal lymphatic pathways, ipilimumab | >28.6 |
| 5 | F | 50 | 02/11 | Left knee, inguinal sentinel lymph node | Right inguinal lymphadenectomy, radiation to the knee and right inguinal | 01/15 | Additive (radiation) | 4 | CR | 23.5 | None | >23.5 |
Table derived from Winkler et al. (2017)
α-CTLA-4 in Post PD1 MCC
- Letter to the editor in the Annals of Oncology
- “Breaking avelumab resistance with combined ipilimumab and nivolumab in metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma?”
- A 60-year-old male with progressive disease on avelumab exhibited a complete response to 4 doses of ipilimumab 1 mg/kg plus nivolumab 3 mg/kg
V. Glutsch et al. (2019)
α-CTLA-4 in Post PD1 MCC
- Dual institutional retrospective report (Johns Hopkins and University of Washington/Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center) of 13 patients previously treated with checkpoint blockade
LoPiccolo et al. (2019)
| Therapies Administered and Corresponding Disease Outcomes | |||||||||
| Case | Patient Age, Sex, MCPyV Status | Therapy #1 | Response #1 | Therapy #2 | Response #2 | Therapy #3 | Response #3 | Therapy #4 | Response #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
irPR at 9 wks PD at 30 wks |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD at 14 wks |
Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks + RT |
PR at 8 wks PD at 12 mos |
| 2 | 79 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 9 wks |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 then Nivolumab 3mg/kg q2wks |
PR at 17 weeks ongoing at 8 mos. Pt died at 10 mos of complications related to encephalopathy |
||||
| 3 | 59 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Pembrolizumab + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 2 months & at 4 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg initially (Pembrolizumab added later) |
Near CR lasting 2 years |
Multiple systemic therapies after Ipilimumab |
PD |
| 4 | 71 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Nivolumab |
CR lasting 26 months then PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab Q6Wks ongoing |
CR lasted 10 months |
||
| 5 | 64 F, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 4 mos |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg IV every 3 weeks |
Died at 10 weeks from PD |
||||
| 6 | 51 M, Unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
CR for 14 mos then PD in CNS only |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD; died at 6 months from leptomeningeal MCC |
||||
| 7 | 67 F, Unknown | RT + Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
RT + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg x 1 |
Ipilimumab discontinued due to toxicity; PD at 3 months |
RT+ Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 2 months |
||
| 8 | 75 M, Unknown | Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 16 wks |
Nivolumab 3mg/kg q3wks + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg q6wks |
PD at ~9 wks |
RT |
Partial regression of irradiated lesions |
||
| 9 | 21 F, Positive | Nivolumab Avelumab |
PD |
Avelumab + IFN + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 1 month |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x1 dose |
PD |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
| 10 | 71 M, Negative | Pembrolizumab |
PR lasting 6 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg + Pembrolizumab x4 doses |
PD at 3 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Pembrolizumab |
PD at 7 months |
||
| 11 | 63 M, Positive | Avelumab +RT+ MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab |
PD at 3 months |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
||
| 12 | 67 M, Negative | Avelumab |
PR lasting 12 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x4 doses |
Stable disease for 3 months |
Nivolumab |
PD at 1 month |
||
| 13 | 63 M, Negative | Adjuvant Avelumab |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x2 doses |
PD |
||||
| Table S1: Therapies administered and corresponding disease outcomes for patients with advanced Merkel cell carcinoma refractory to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1. (CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; irPR, immune-related partial response; MCPyV, Merkel cell polyomavirus; PD, progressive disease; RT, radiotherapy) | |||||||||
Table derived from LoPiccolo et al. (2019)
| Therapies Administered and Corresponding Disease Outcomes | |||||||||
| Case | Patient Age, Sex, MCPyV Status | Therapy #1 | Response #1 | Therapy #2 | Response #2 | Therapy #3 | Response #3 | Therapy #4 | Response #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
irPR at 9 wks PD at 30 wks |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD at 14 wks |
Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks + RT |
PR at 8 wks PD at 12 mos |
| 2 | 79 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 9 wks |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 then Nivolumab 3mg/kg q2wks |
PR at 17 weeks ongoing at 8 mos. Pt died at 10 mos of complications related to encephalopathy |
||||
| 3 | 59 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Pembrolizumab + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 2 months & at 4 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg initially (Pembrolizumab added later) |
Near CR lasting 2 years |
Multiple systemic therapies after Ipilimumab |
PD |
| 4 | 71 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Nivolumab |
CR lasting 26 months then PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab Q6Wks ongoing |
CR lasted 10 months |
||
| 5 | 64 F, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 4 mos |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg IV every 3 weeks |
Died at 10 weeks from PD |
||||
| 6 | 51 M, Unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
CR for 14 mos then PD in CNS only |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD; died at 6 months from leptomeningeal MCC |
||||
| 7 | 67 F, Unknown | RT + Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
RT + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg x 1 |
Ipilimumab discontinued due to toxicity; PD at 3 months |
RT+ Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 2 months |
||
| 8 | 75 M, Unknown | Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 16 wks |
Nivolumab 3mg/kg q3wks + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg q6wks |
PD at ~9 wks |
RT |
Partial regression of irradiated lesions |
||
| 9 | 21 F, Positive | Nivolumab Avelumab |
PD |
Avelumab + IFN + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 1 month |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x1 dose |
PD |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
| 10 | 71 M, Negative | Pembrolizumab |
PR lasting 6 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg + Pembrolizumab x4 doses |
PD at 3 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Pembrolizumab |
PD at 7 months |
||
| 11 | 63 M, Positive | Avelumab +RT+ MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab |
PD at 3 months |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
||
| 12 | 67 M, Negative | Avelumab |
PR lasting 12 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x4 doses |
Stable disease for 3 months |
Nivolumab |
PD at 1 month |
||
| 13 | 63 M, Negative | Adjuvant Avelumab |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x2 doses |
PD |
||||
| Table S1: Therapies administered and corresponding disease outcomes for patients with advanced Merkel cell carcinoma refractory to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1. (CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; irPR, immune-related partial response; MCPyV, Merkel cell polyomavirus; PD, progressive disease; RT, radiotherapy) | |||||||||
Table derived from LoPiccolo et al. (2019)
| Therapies Administered and Corresponding Disease Outcomes | |||||||||
| Case | Patient Age, Sex, MCPyV Status | Therapy #1 | Response #1 | Therapy #2 | Response #2 | Therapy #3 | Response #3 | Therapy #4 | Response #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
irPR at 9 wks PD at 30 wks |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD at 14 wks |
Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks + RT |
PR at 8 wks PD at 12 mos |
| 2 | 79 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 9 wks |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 then Nivolumab 3mg/kg q2wks |
PR at 17 weeks ongoing at 8 mos. Pt died at 10 mos of complications related to encephalopathy |
||||
| 3 | 59 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Pembrolizumab + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 2 months & at 4 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg initially (Pembrolizumab added later) |
Near CR lasting 2 years |
Multiple systemic therapies after Ipilimumab |
PD |
| 4 | 71 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Nivolumab |
CR lasting 26 months then PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab Q6Wks ongoing |
CR lasted 10 months |
||
| 5 | 64 F, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 4 mos |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg IV every 3 weeks |
Died at 10 weeks from PD |
||||
| 6 | 51 M, Unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
CR for 14 mos then PD in CNS only |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD; died at 6 months from leptomeningeal MCC |
||||
| 7 | 67 F, Unknown | RT + Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
RT + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg x 1 |
Ipilimumab discontinued due to toxicity; PD at 3 months |
RT+ Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 2 months |
||
| 8 | 75 M, Unknown | Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 16 wks |
Nivolumab 3mg/kg q3wks + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg q6wks |
PD at ~9 wks |
RT |
Partial regression of irradiated lesions |
||
| 9 | 21 F, Positive | Nivolumab Avelumab |
PD |
Avelumab + IFN + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 1 month |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x1 dose |
PD |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
| 10 | 71 M, Negative | Pembrolizumab |
PR lasting 6 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg + Pembrolizumab x4 doses |
PD at 3 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Pembrolizumab |
PD at 7 months |
||
| 11 | 63 M, Positive | Avelumab +RT+ MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab |
PD at 3 months |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
||
| 12 | 67 M, Negative | Avelumab |
PR lasting 12 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x4 doses |
Stable disease for 3 months |
Nivolumab |
PD at 1 month |
||
| 13 | 63 M, Negative | Adjuvant Avelumab |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x2 doses |
PD |
||||
| Table S1: Therapies administered and corresponding disease outcomes for patients with advanced Merkel cell carcinoma refractory to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1. (CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; irPR, immune-related partial response; MCPyV, Merkel cell polyomavirus; PD, progressive disease; RT, radiotherapy) | |||||||||
Table derived from LoPiccolo et al. (2019)
| Therapies Administered and Corresponding Disease Outcomes | |||||||||
| Case | Patient Age, Sex, MCPyV Status | Therapy #1 | Response #1 | Therapy #2 | Response #2 | Therapy #3 | Response #3 | Therapy #4 | Response #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
irPR at 9 wks PD at 30 wks |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD at 14 wks |
Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks + RT |
PR at 8 wks PD at 12 mos |
| 2 | 79 M, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 9 wks |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 then Nivolumab 3mg/kg q2wks |
PR at 17 weeks ongoing at 8 mos. Pt died at 10 mos of complications related to encephalopathy |
||||
| 3 | 59 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Pembrolizumab + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 2 months & at 4 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg initially (Pembrolizumab added later) |
Near CR lasting 2 years |
Multiple systemic therapies after Ipilimumab |
PD |
| 4 | 71 M, Positive | Multiple systemic therapies prior to anti PD-1 |
Variable |
Nivolumab |
CR lasting 26 months then PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab Q6Wks ongoing |
CR lasted 10 months |
||
| 5 | 64 F, unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 4 mos |
Ipilimumab 3mg/kg IV every 3 weeks |
Died at 10 weeks from PD |
||||
| 6 | 51 M, Unknown | Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
CR for 14 mos then PD in CNS only |
RT + Ipilimumab 3mg/kg + Nivolumab 1mg/kg q3wks x 4 |
PD; died at 6 months from leptomeningeal MCC |
||||
| 7 | 67 F, Unknown | RT + Pembrolizumab 2mg/kg q3wks |
PD at 2 months |
RT + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg x 1 |
Ipilimumab discontinued due to toxicity; PD at 3 months |
RT+ Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 2 months |
||
| 8 | 75 M, Unknown | Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks |
PD at 16 wks |
Nivolumab 3mg/kg q3wks + Ipilimumab 1mg/kg q6wks |
PD at ~9 wks |
RT |
Partial regression of irradiated lesions |
||
| 9 | 21 F, Positive | Nivolumab Avelumab |
PD |
Avelumab + IFN + MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD at 1 month |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x1 dose |
PD |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
| 10 | 71 M, Negative | Pembrolizumab |
PR lasting 6 months |
Ipilimumab 0.5mg/kg + Pembrolizumab x4 doses |
PD at 3 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Pembrolizumab |
PD at 7 months |
||
| 11 | 63 M, Positive | Avelumab +RT+ MCPyV-specific T cells |
PD |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab |
PD at 3 months |
Multiple systemic therapies |
PD |
||
| 12 | 67 M, Negative | Avelumab |
PR lasting 12 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x4 doses |
Stable disease for 3 months |
Nivolumab |
PD at 1 month |
||
| 13 | 63 M, Negative | Adjuvant Avelumab |
PD at 2 months |
Ipilimumab 1mg/kg + Nivolumab x2 doses |
PD |
||||
| Table S1: Therapies administered and corresponding disease outcomes for patients with advanced Merkel cell carcinoma refractory to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1. (CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; irPR, immune-related partial response; MCPyV, Merkel cell polyomavirus; PD, progressive disease; RT, radiotherapy) | |||||||||
Table derived from LoPiccolo et al. (2019)
| Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in the Post PD-1/PD-L1 Setting in MCC | |||||||
| Therapy | Study | N | Objective Response (%) | Complete Response (%) | Median DOR (months) | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ipilimumab +/- anti-PD1 | Hopkins/Fred Hutch Retrospective | 13 | 31 | 15.4 | NA | NA | NA |
|
References:
|
|||||||
α-CTLA-4 in Post PD1 MCC
- Dual institutional retrospective report (BWH/DFCI and MGH) of 13 patients previously treated with checkpoint blockade
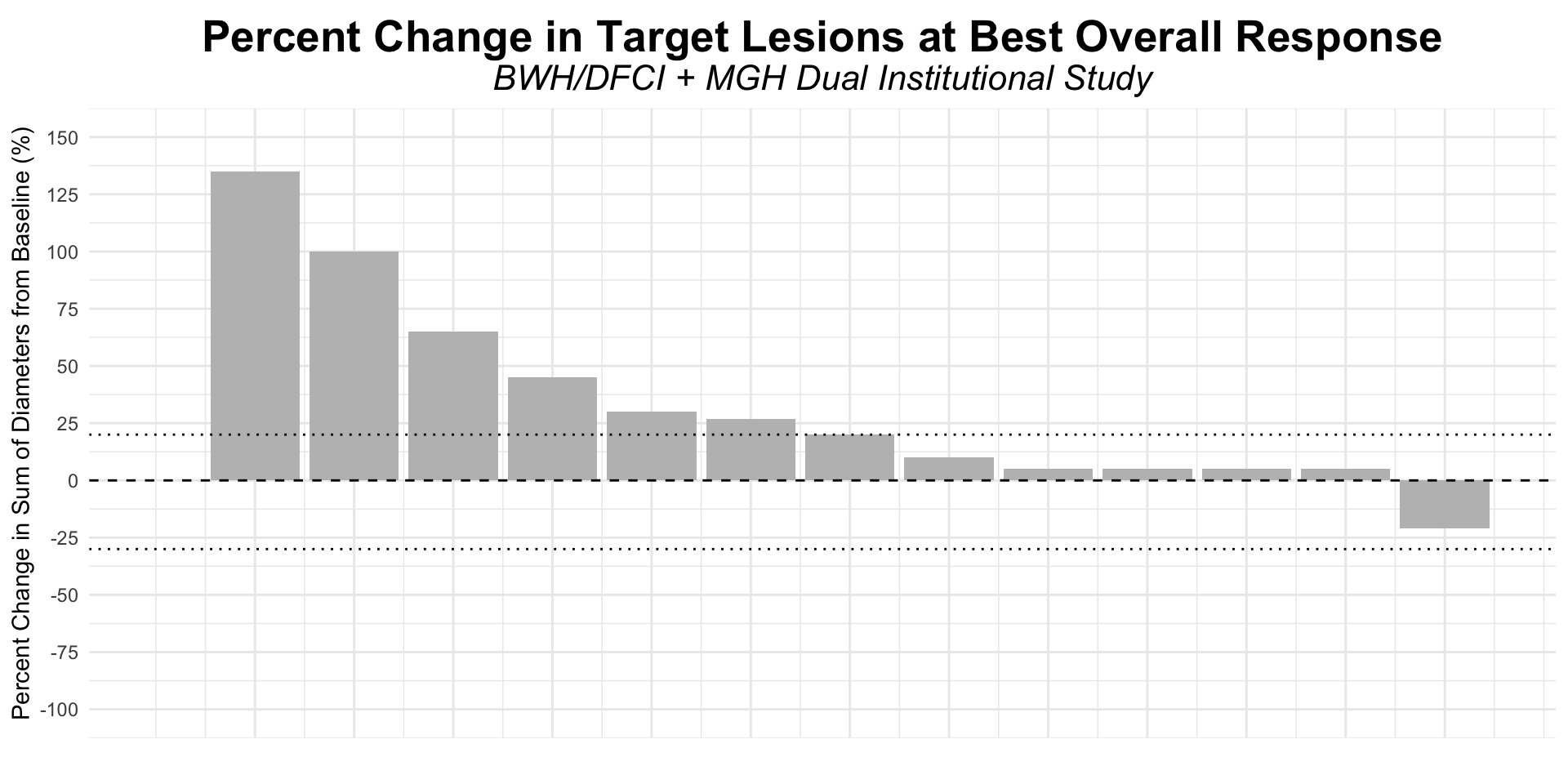
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
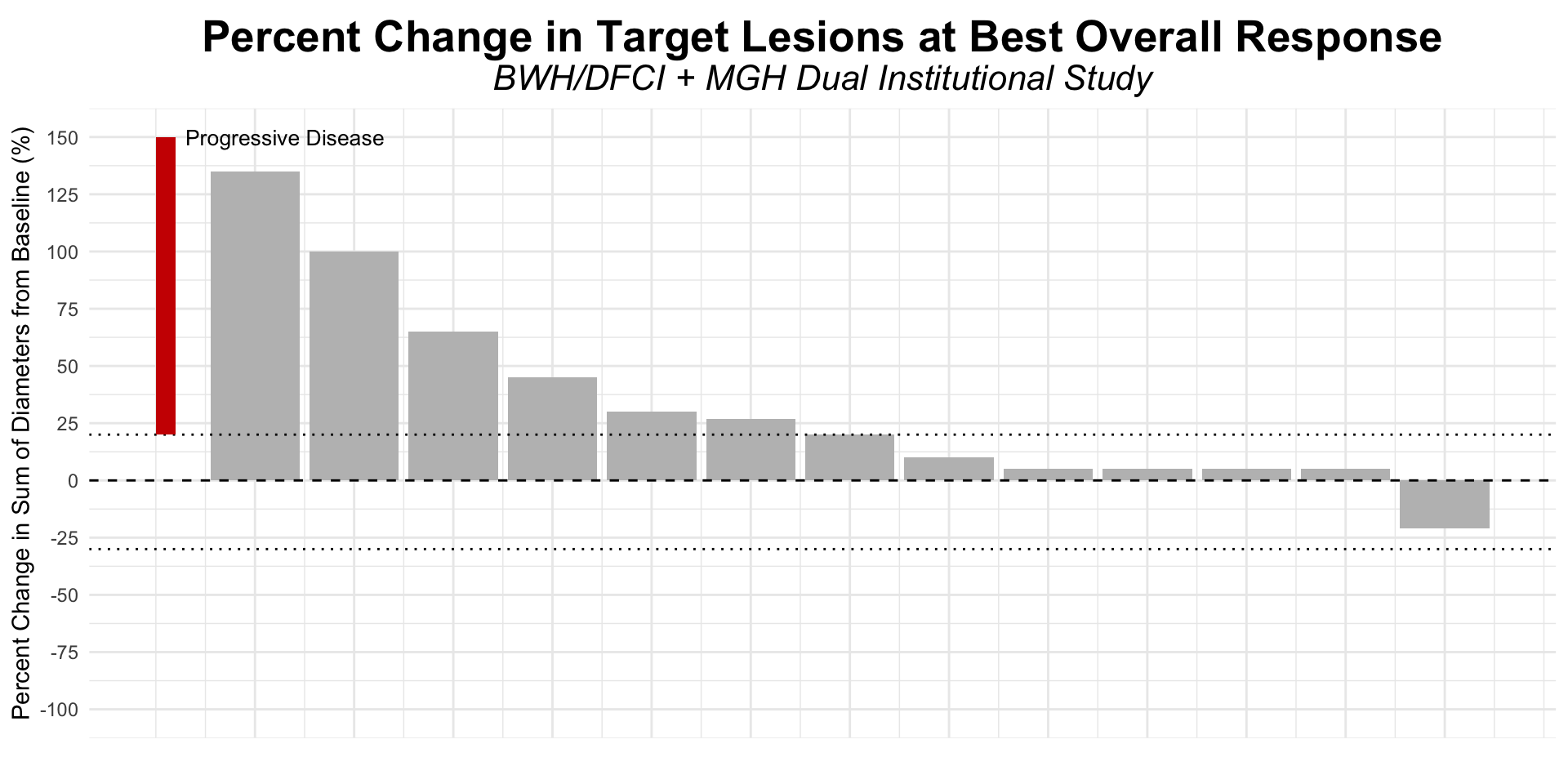
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
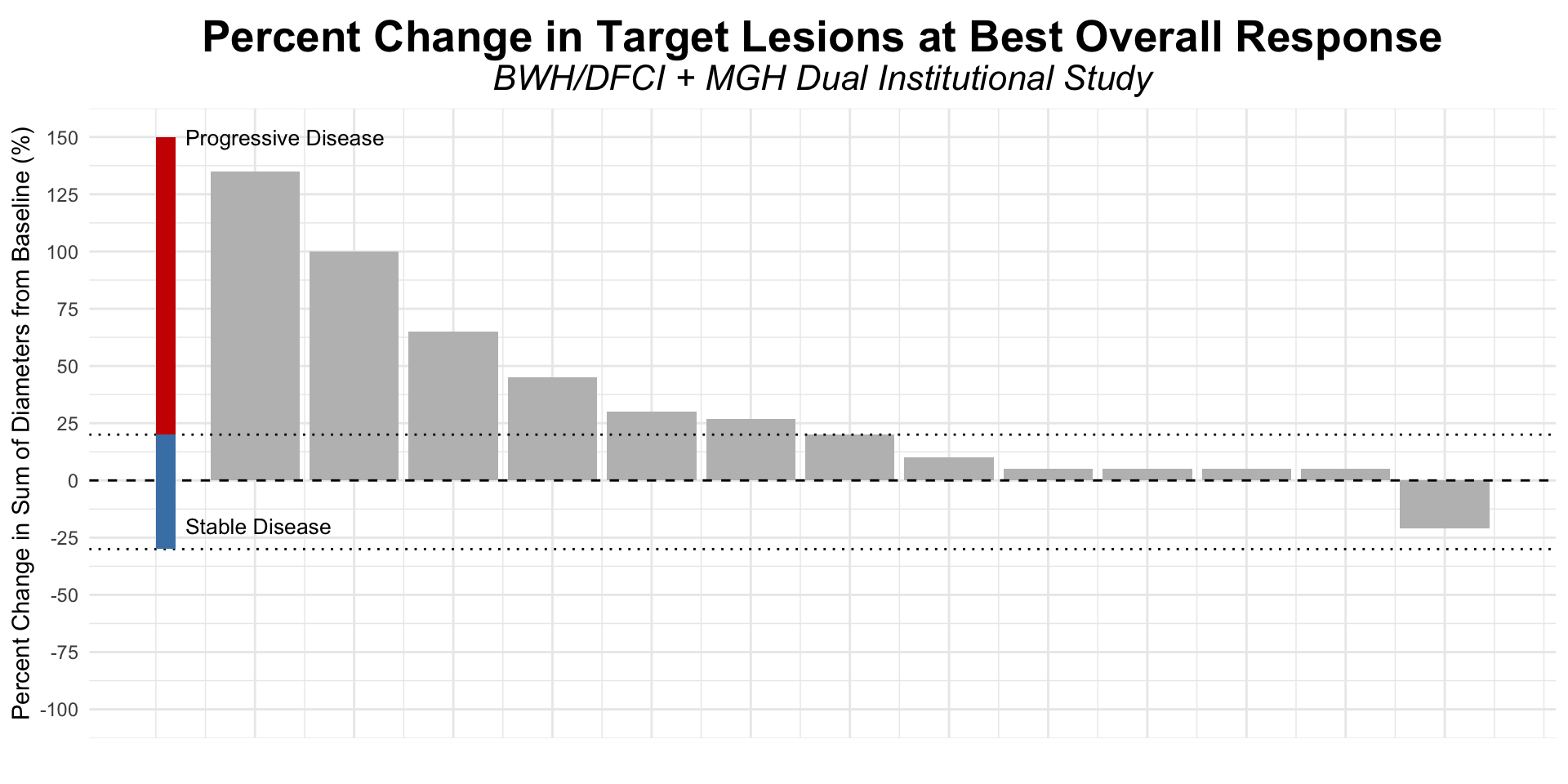
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
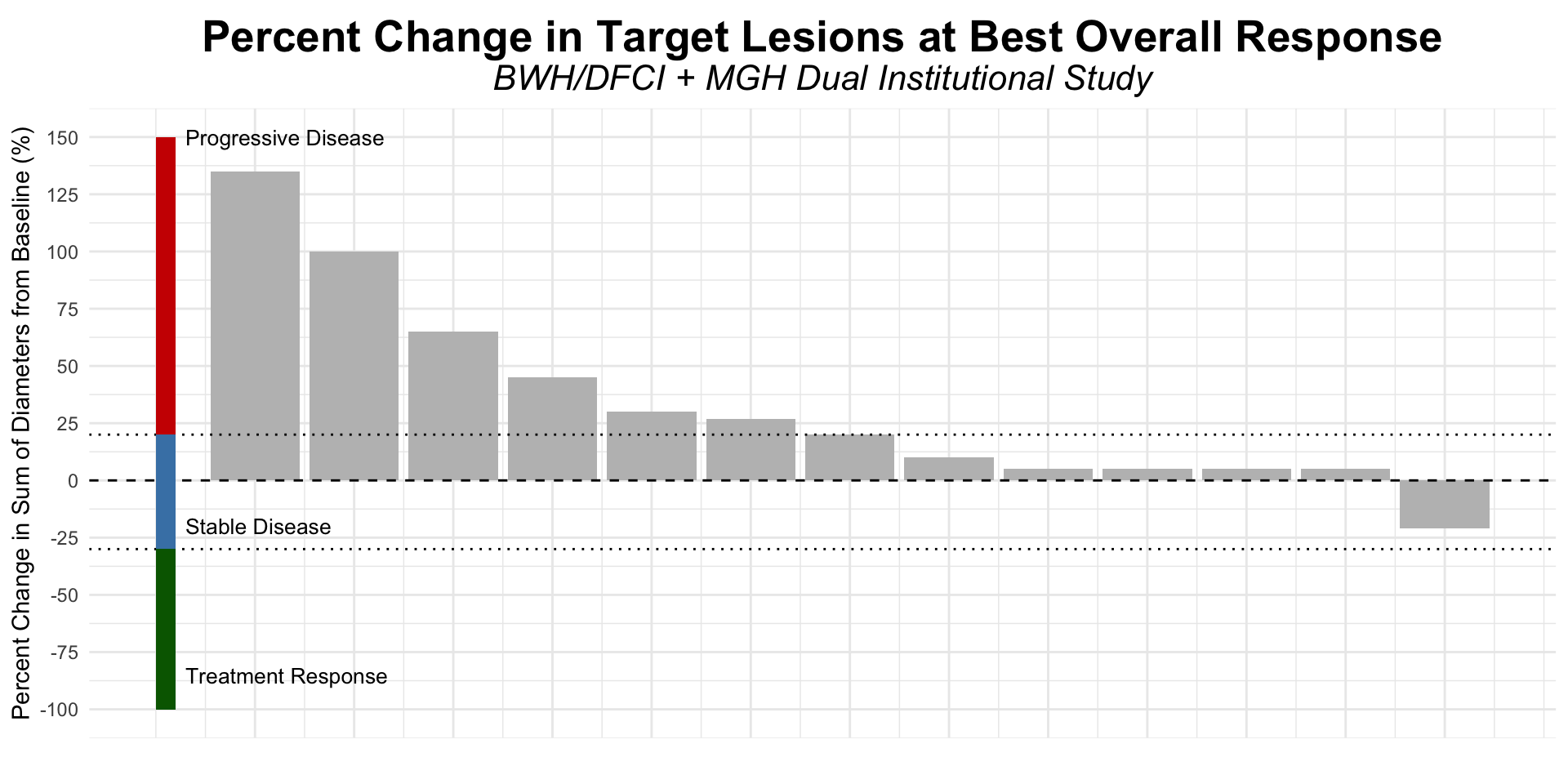
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
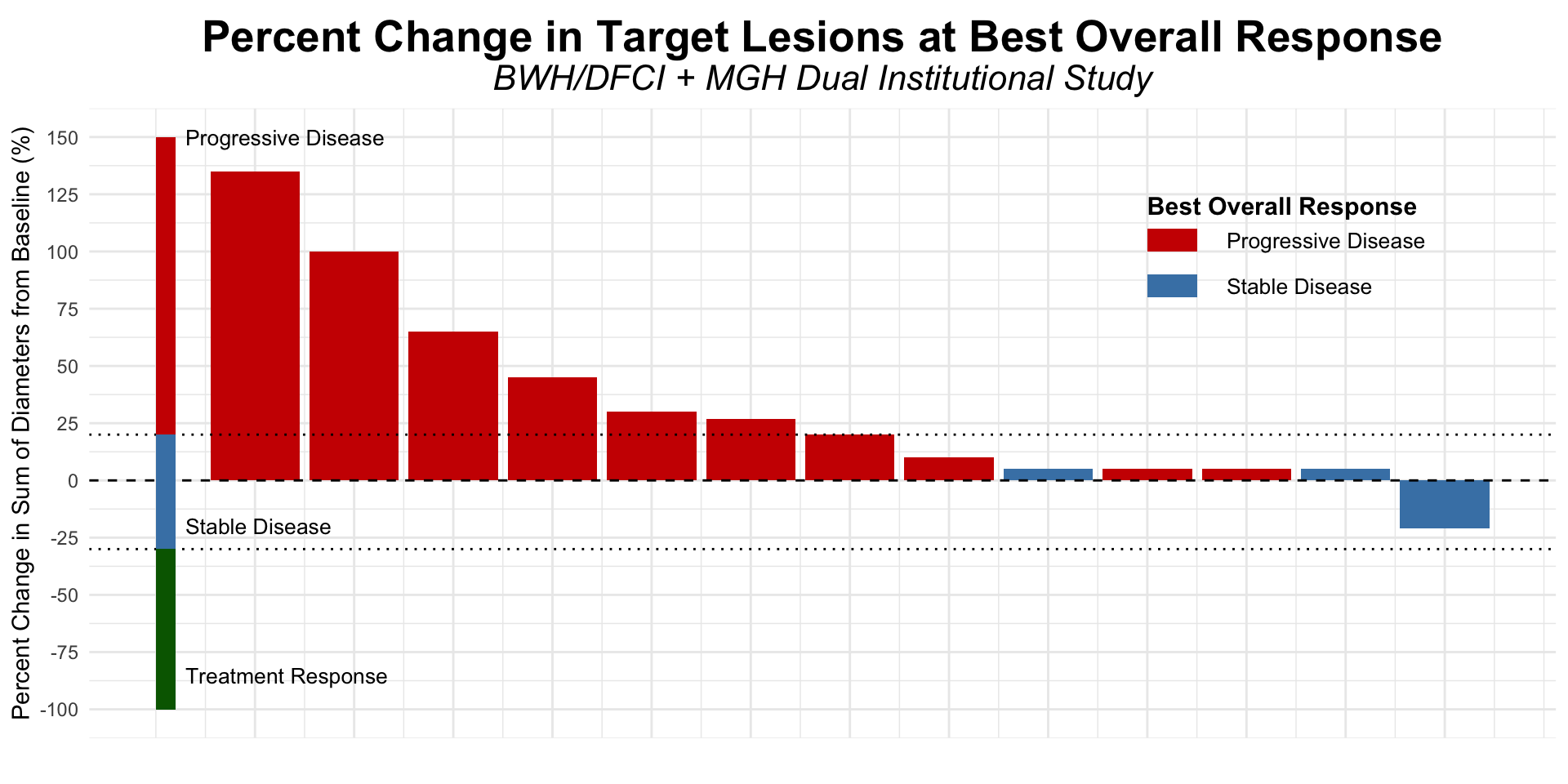
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
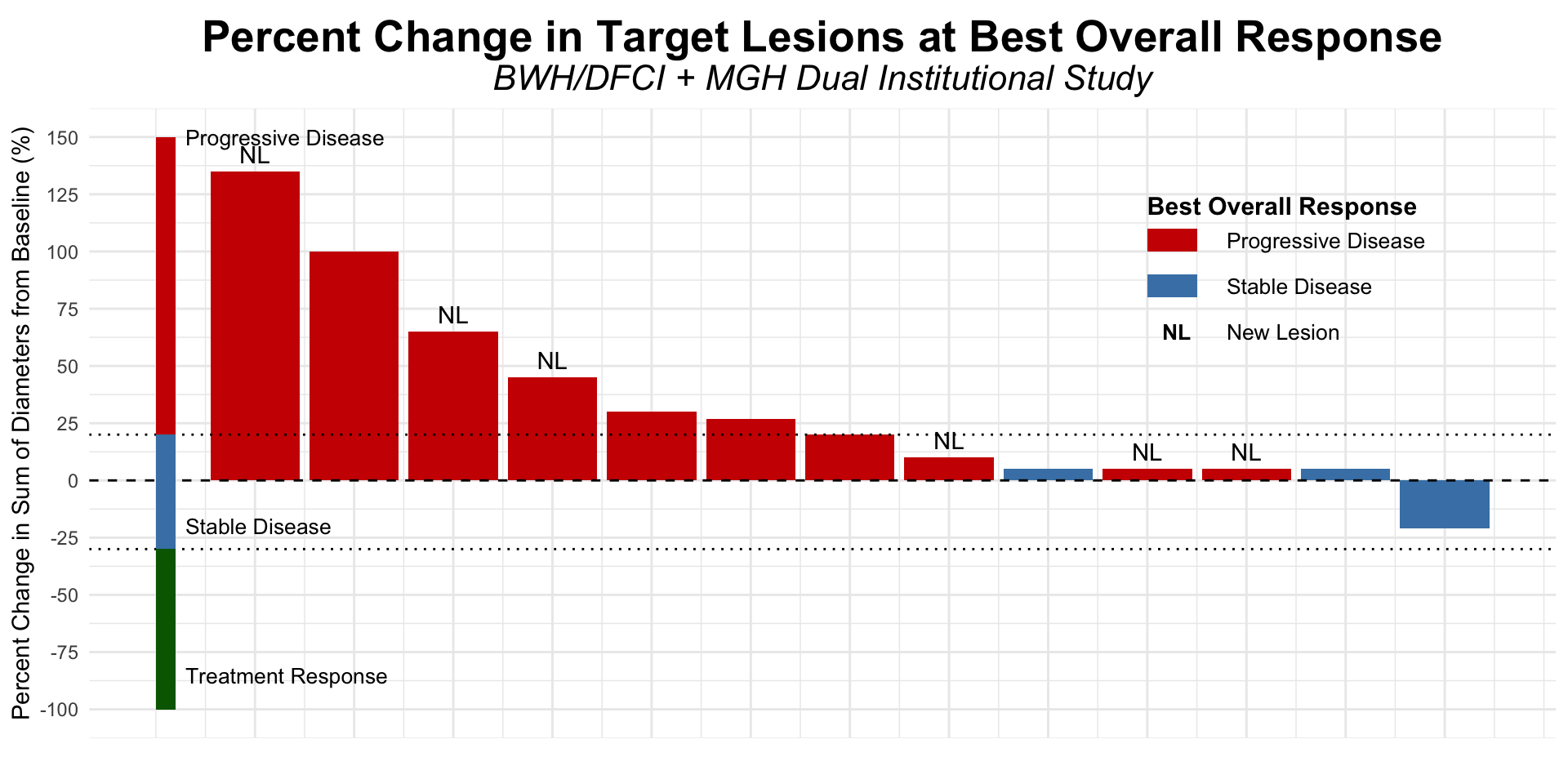
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
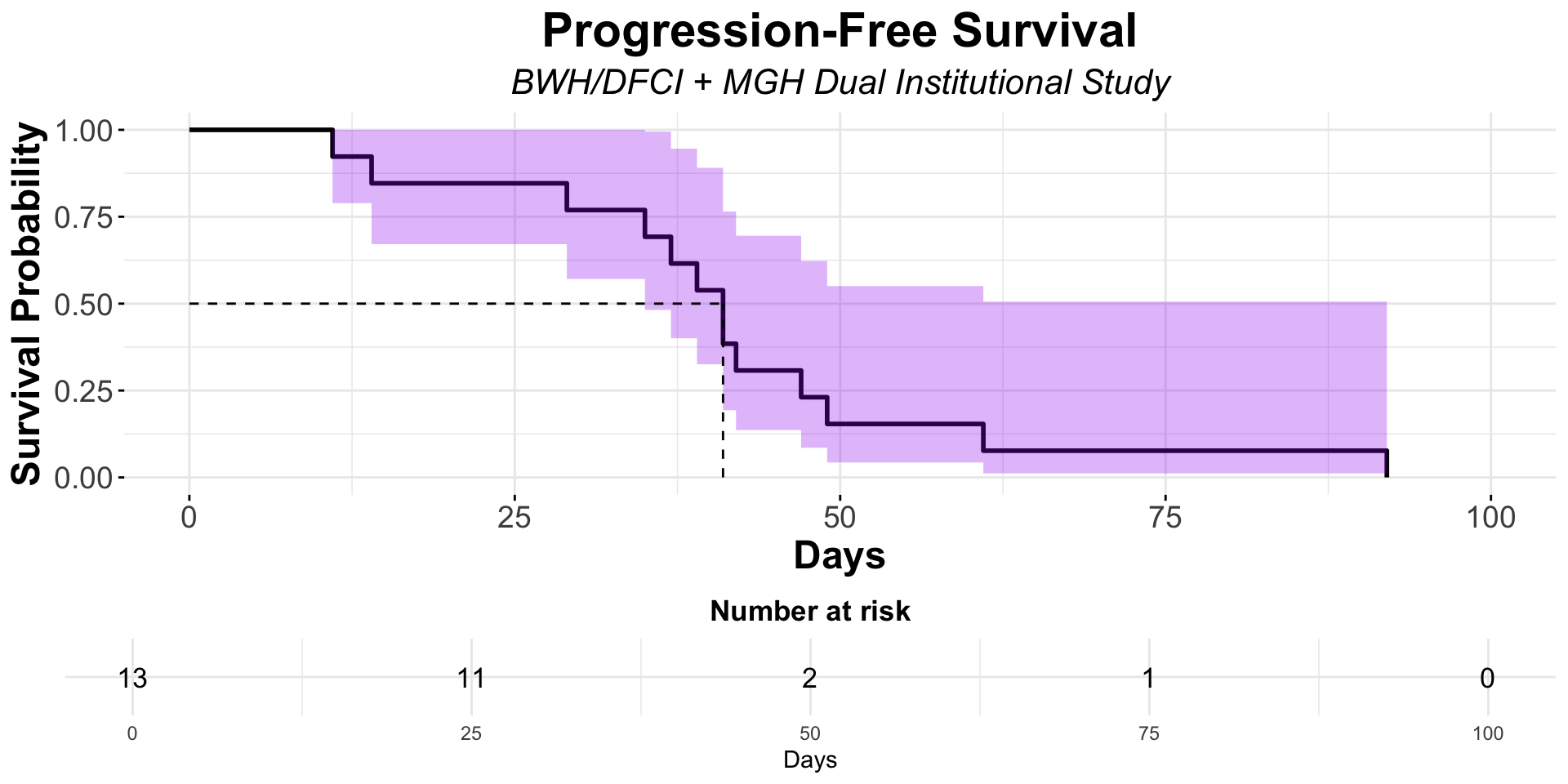
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
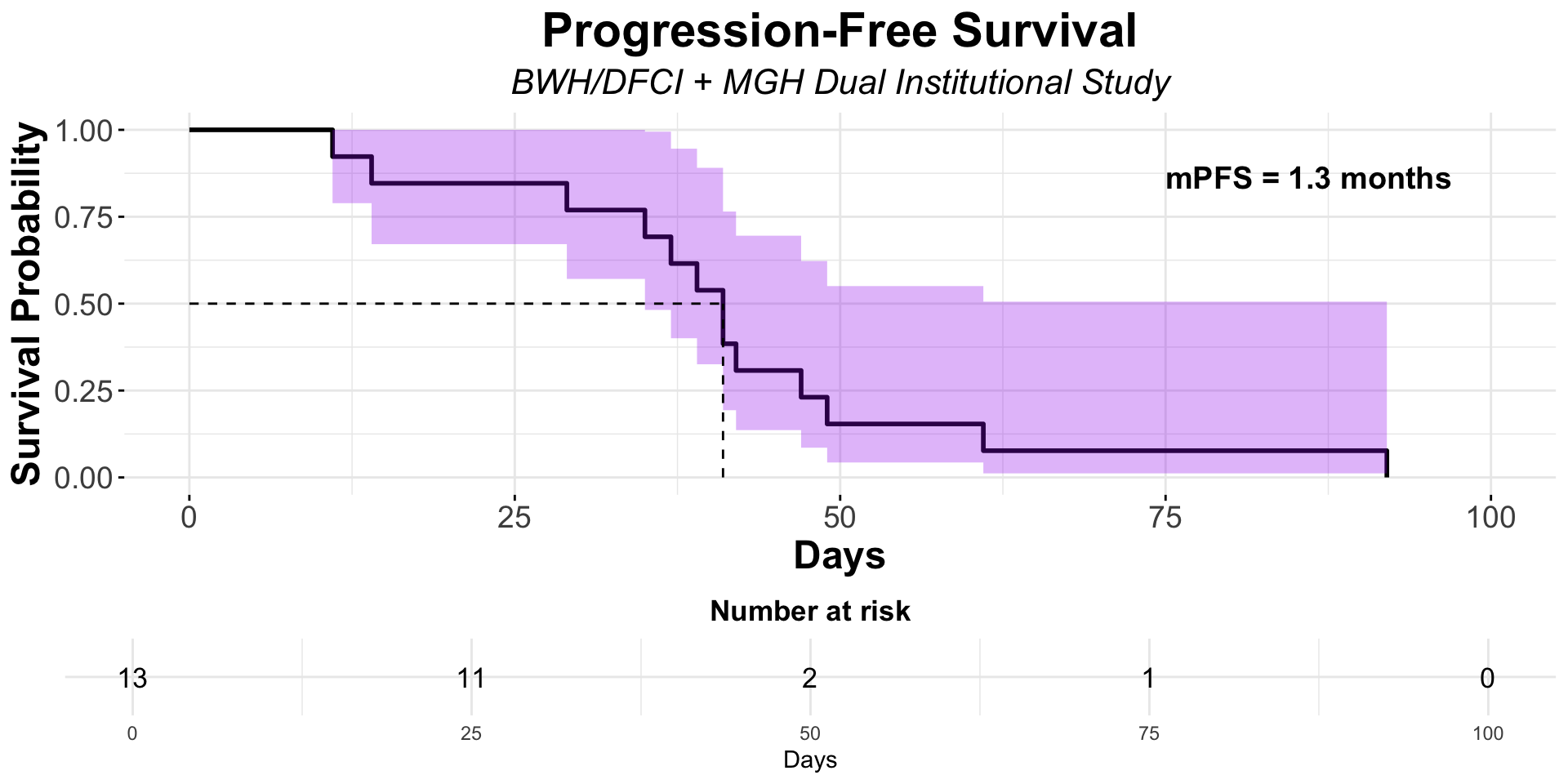
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
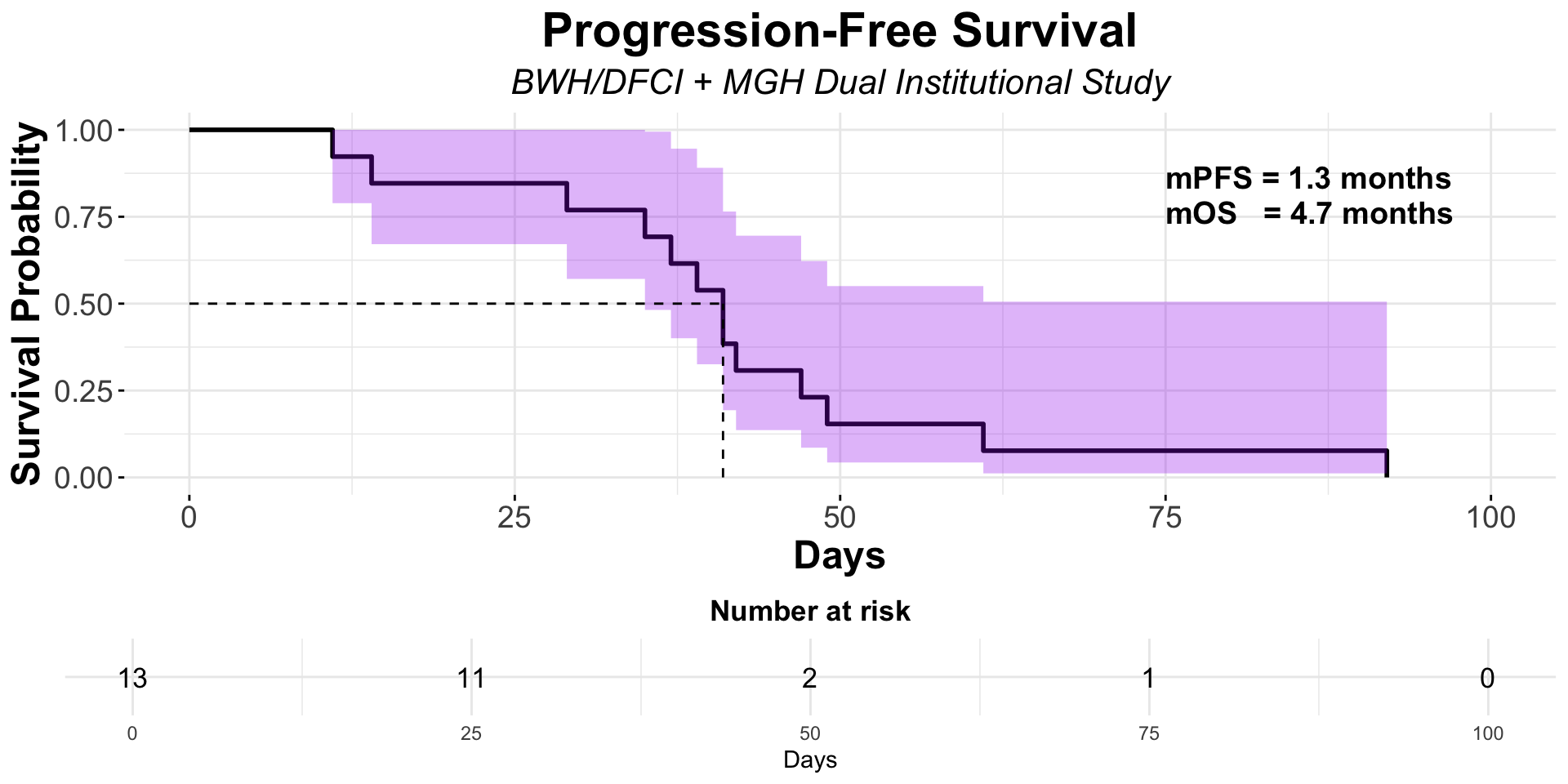
Figure redrawn from Shalhout et al. (2022)
α-CTLA-4 in Post PD1 MCC
- Report of 14 patients from the multi-center institutional skin cancer registry ADOREG
Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
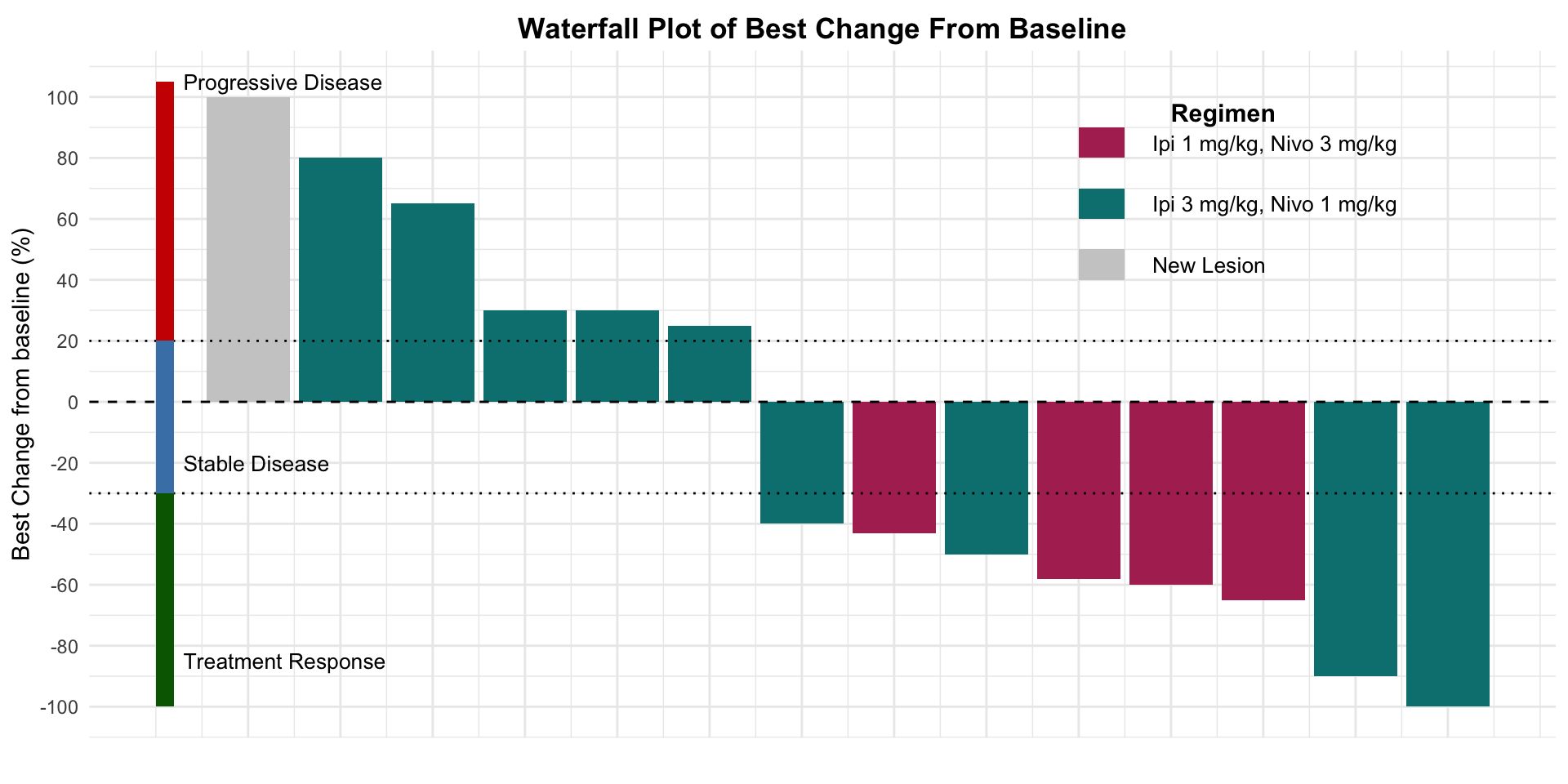
Figure redrawn from Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
| Outcome Associated with Later-Line IPI/NIVO | |
| Outcome | Results |
|---|---|
| IPI/NIVO | |
| BOR | |
| CR 1/14 | 7.1% (1/14) |
| PR 6/14 | 42.9% (6/14) |
| SD 0/14 | 0% (0/14) |
| PD 7/14 | 50% (7/14) |
| PFS | |
| Median (range) | 5.07 (2.43–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 42.9 (23.4 to 78.5) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 26.8 (10.9 to 66.0) |
| OS | |
| Median (range) | NR (3.75–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 3-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| Median follow-up (months) (IQR) | 18.85 (17.63–22.40) |
Table derived from Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
| Outcome Associated with Later-Line IPI/NIVO | |
| Outcome | Results |
|---|---|
| IPI/NIVO | |
| BOR | |
| CR 1/14 | 7.1% (1/14) |
| PR 6/14 | 42.9% (6/14) |
| SD 0/14 | 0% (0/14) |
| PD 7/14 | 50% (7/14) |
| PFS | |
| Median (range) | 5.07 (2.43–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 42.9 (23.4 to 78.5) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 26.8 (10.9 to 66.0) |
| OS | |
| Median (range) | NR (3.75–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 3-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| Median follow-up (months) (IQR) | 18.85 (17.63–22.40) |
Table derived from Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
| Outcome Associated with Later-Line IPI/NIVO | |
| Outcome | Results |
|---|---|
| IPI/NIVO | |
| BOR | |
| CR 1/14 | 7.1% (1/14) |
| PR 6/14 | 42.9% (6/14) |
| SD 0/14 | 0% (0/14) |
| PD 7/14 | 50% (7/14) |
| PFS | |
| Median (range) | 5.07 (2.43–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 42.9 (23.4 to 78.5) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 26.8 (10.9 to 66.0) |
| OS | |
| Median (range) | NR (3.75–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 3-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| Median follow-up (months) (IQR) | 18.85 (17.63–22.40) |
Table derived from Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
| Outcome Associated with Later-Line IPI/NIVO | |
| Outcome | Results |
|---|---|
| IPI/NIVO | |
| BOR | |
| CR 1/14 | 7.1% (1/14) |
| PR 6/14 | 42.9% (6/14) |
| SD 0/14 | 0% (0/14) |
| PD 7/14 | 50% (7/14) |
| PFS | |
| Median (range) | 5.07 (2.43–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 42.9 (23.4 to 78.5) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 26.8 (10.9 to 66.0) |
| OS | |
| Median (range) | NR (3.75–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 3-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| Median follow-up (months) (IQR) | 18.85 (17.63–22.40) |
Table derived from Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
| Outcome Associated with Later-Line IPI/NIVO | |
| Outcome | Results |
|---|---|
| IPI/NIVO | |
| BOR | |
| CR 1/14 | 7.1% (1/14) |
| PR 6/14 | 42.9% (6/14) |
| SD 0/14 | 0% (0/14) |
| PD 7/14 | 50% (7/14) |
| PFS | |
| Median (range) | 5.07 (2.43–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 42.9 (23.4 to 78.5) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 26.8 (10.9 to 66.0) |
| OS | |
| Median (range) | NR (3.75–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 3-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| Median follow-up (months) (IQR) | 18.85 (17.63–22.40) |
Table derived from Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
| Outcome Associated with Later-Line IPI/NIVO | |
| Outcome | Results |
|---|---|
| IPI/NIVO | |
| BOR | |
| CR 1/14 | 7.1% (1/14) |
| PR 6/14 | 42.9% (6/14) |
| SD 0/14 | 0% (0/14) |
| PD 7/14 | 50% (7/14) |
| PFS | |
| Median (range) | 5.07 (2.43–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 42.9 (23.4 to 78.5) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 26.8 (10.9 to 66.0) |
| OS | |
| Median (range) | NR (3.75–NA) |
| 1-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 2-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| 3-year rate (%) (95% CI) | 64.3 (43.5 to 95.0) |
| Median follow-up (months) (IQR) | 18.85 (17.63–22.40) |
Table derived from Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022)
α-CTLA-4 in Post PD1 MCC
- Dual institution (Moffitt Cancer Center and the Ohio State University James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute ) prospective clinical trial of 26 patients
Kim et al. (2022)
| Objective Response and Durability of Response | ||||||
| Outcome Measures | Total | Group A (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab) | Group B (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab plus SBRT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICI Naive (n=24) | Previous ICI (n=26) | ICI Naive (n=13) | Previous ICI (n=12) | ICI Naive (n=11) | Previous ICI (n=14) | |
| ORR (95% CI)1 | 100 (82–100) | 31 (15–52) | 100% (72–100) | 42% (16–71) | 100% (63–100) | 21% (6–51) |
| BOR | ||||||
| CR | 9/22 (41%) | 4 (15%) | 7 (54%) | 3 (25%) | 2/9 (22%) | 1 (7%) |
| PR | 13/22 (59%) | 4 (15%) | 6 (46%) | 2 (17%) | 7/9 (78%) | 2 (14%) |
| SD | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 |
| PD | 0 | 17 (65%) | 0 | 6 (50%) | 0 | 11 (79%) |
| Median PFS (months) | NR | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | |
| Median OS (months) | NR | NR | 14.9 (0.3-NE) | NR | 9.7 (5.0-NE) | |
| 1 Data are n (%) unless otherwise stated. Percentages are rounded to the nearest whole number. BOR=best overall response. CR=complete response. DOR=duration of response. ICI=immune-checkpoint inhibitor.NE=non-estimable. ORR=objective response rate. PD=progressive disease. PR=partial response. SBRT=stereotactic body radiotherapy. SD=stable disease. *Two partial responders in the previous-ICI cohort had unconfirmed partial responses. †Two patients deemed non-evaluable as the target lesion was irradiated. ‡Includes 30 responders with at least 6 months of follow-up. | ||||||
Table derived from Kim et al. (2022)
| Objective Response and Durability of Response | ||||||
| Outcome Measures | Total | Group A (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab) | Group B (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab plus SBRT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICI Naive (n=24) | Previous ICI (n=26) | ICI Naive (n=13) | Previous ICI (n=12) | ICI Naive (n=11) | Previous ICI (n=14) | |
| ORR (95% CI)1 | 100 (82–100) | 31 (15–52) | 100% (72–100) | 42% (16–71) | 100% (63–100) | 21% (6–51) |
| BOR | ||||||
| CR | 9/22 (41%) | 4 (15%) | 7 (54%) | 3 (25%) | 2/9 (22%) | 1 (7%) |
| PR | 13/22 (59%) | 4 (15%) | 6 (46%) | 2 (17%) | 7/9 (78%) | 2 (14%) |
| SD | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 |
| PD | 0 | 17 (65%) | 0 | 6 (50%) | 0 | 11 (79%) |
| Median PFS (months) | NR | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | |
| Median OS (months) | NR | NR | 14.9 (0.3-NE) | NR | 9.7 (5.0-NE) | |
| 1 Data are n (%) unless otherwise stated. Percentages are rounded to the nearest whole number. BOR=best overall response. CR=complete response. DOR=duration of response. ICI=immune-checkpoint inhibitor.NE=non-estimable. ORR=objective response rate. PD=progressive disease. PR=partial response. SBRT=stereotactic body radiotherapy. SD=stable disease. *Two partial responders in the previous-ICI cohort had unconfirmed partial responses. †Two patients deemed non-evaluable as the target lesion was irradiated. ‡Includes 30 responders with at least 6 months of follow-up. | ||||||
Table derived from Kim et al. (2022)
| Objective Response and Durability of Response | ||||||
| Outcome Measures | Total | Group A (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab) | Group B (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab plus SBRT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICI Naive (n=24) | Previous ICI (n=26) | ICI Naive (n=13) | Previous ICI (n=12) | ICI Naive (n=11) | Previous ICI (n=14) | |
| ORR (95% CI)1 | 100 (82–100) | 31 (15–52) | 100% (72–100) | 42% (16–71) | 100% (63–100) | 21% (6–51) |
| BOR | ||||||
| CR | 9/22 (41%) | 4 (15%) | 7 (54%) | 3 (25%) | 2/9 (22%) | 1 (7%) |
| PR | 13/22 (59%) | 4 (15%) | 6 (46%) | 2 (17%) | 7/9 (78%) | 2 (14%) |
| SD | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 |
| PD | 0 | 17 (65%) | 0 | 6 (50%) | 0 | 11 (79%) |
| Median PFS (months) | NR | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | |
| Median OS (months) | NR | NR | 14.9 (0.3-NE) | NR | 9.7 (5.0-NE) | |
| 1 Data are n (%) unless otherwise stated. Percentages are rounded to the nearest whole number. BOR=best overall response. CR=complete response. DOR=duration of response. ICI=immune-checkpoint inhibitor.NE=non-estimable. ORR=objective response rate. PD=progressive disease. PR=partial response. SBRT=stereotactic body radiotherapy. SD=stable disease. *Two partial responders in the previous-ICI cohort had unconfirmed partial responses. †Two patients deemed non-evaluable as the target lesion was irradiated. ‡Includes 30 responders with at least 6 months of follow-up. | ||||||
Table derived from Kim et al. (2022)
| Objective Response and Durability of Response | ||||||
| Outcome Measures | Total | Group A (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab) | Group B (combined nivolumab and ipilimumab plus SBRT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICI Naive (n=24) | Previous ICI (n=26) | ICI Naive (n=13) | Previous ICI (n=12) | ICI Naive (n=11) | Previous ICI (n=14) | |
| ORR (95% CI)1 | 100 (82–100) | 31 (15–52) | 100% (72–100) | 42% (16–71) | 100% (63–100) | 21% (6–51) |
| BOR | ||||||
| CR | 9/22 (41%) | 4 (15%) | 7 (54%) | 3 (25%) | 2/9 (22%) | 1 (7%) |
| PR | 13/22 (59%) | 4 (15%) | 6 (46%) | 2 (17%) | 7/9 (78%) | 2 (14%) |
| SD | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 |
| PD | 0 | 17 (65%) | 0 | 6 (50%) | 0 | 11 (79%) |
| Median PFS (months) | NR | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | NR | 2.7 (2.2-7.6) | |
| Median OS (months) | NR | NR | 14.9 (0.3-NE) | NR | 9.7 (5.0-NE) | |
| 1 Data are n (%) unless otherwise stated. Percentages are rounded to the nearest whole number. BOR=best overall response. CR=complete response. DOR=duration of response. ICI=immune-checkpoint inhibitor.NE=non-estimable. ORR=objective response rate. PD=progressive disease. PR=partial response. SBRT=stereotactic body radiotherapy. SD=stable disease. *Two partial responders in the previous-ICI cohort had unconfirmed partial responses. †Two patients deemed non-evaluable as the target lesion was irradiated. ‡Includes 30 responders with at least 6 months of follow-up. | ||||||
Table derived from Kim et al. (2022)
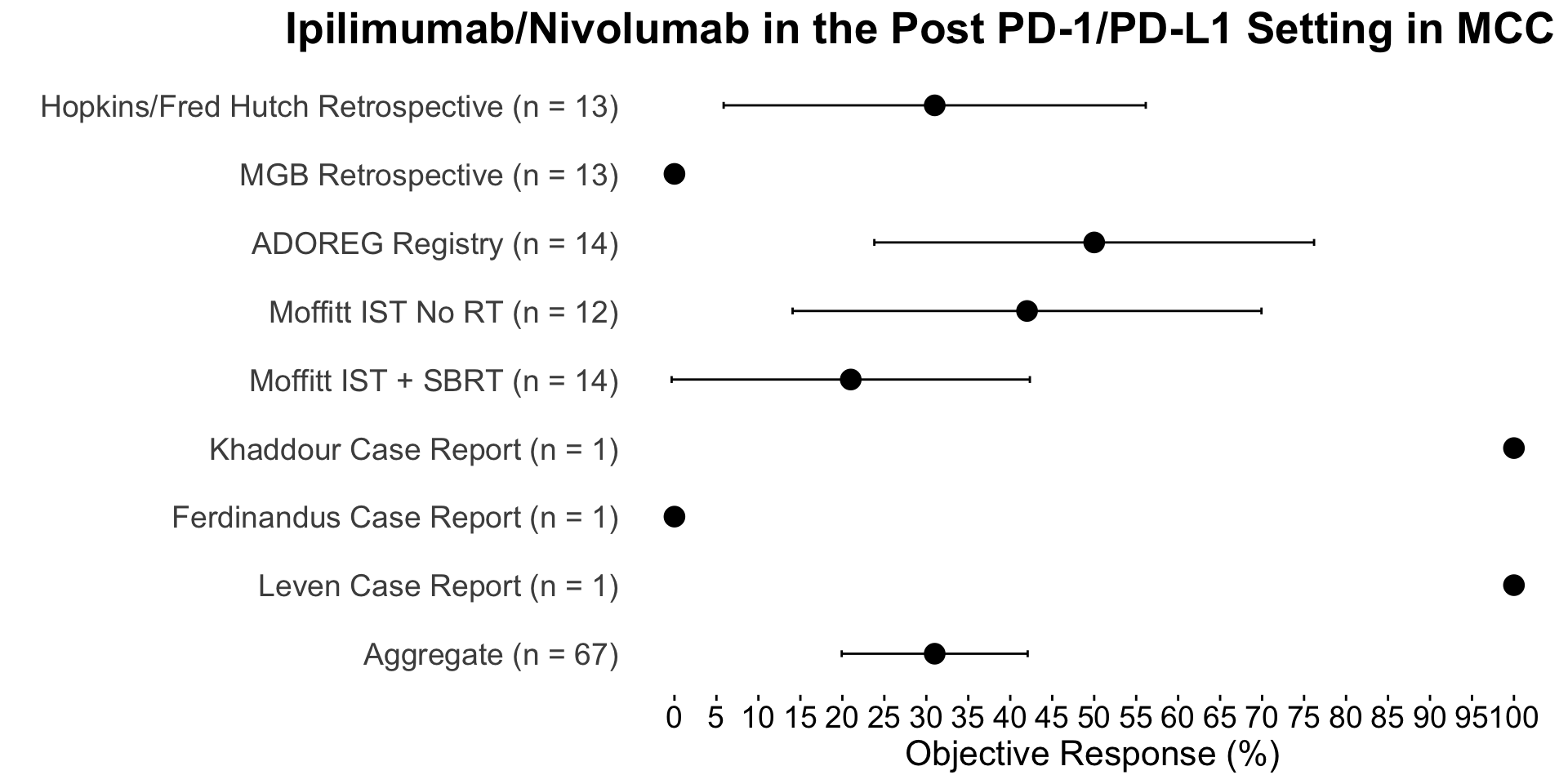
| Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in the Post PD-1/PD-L1 Setting in MCC | |||||||
| Therapy | Study | N | Objective Response (%) | Complete Response (%) | Median DOR (months) | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ipilimumab +/- anti-PD1 | Hopkins/Fred Hutch Retrospective | 13 | 31 | 15 | NA | NA | NA |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | MGB Retrospective1 | 13 | 0 | 0 | NA | 1.3 | 4.7 |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | ADOREG Registry2 | 14 | 50 | 7 | NA | 5.07 | NR |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Moffitt IST No RT3 | 12 | 42 | 25 | 15.1 | 4.2 | 14.9 |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab + RT | Moffitt IST + SBRT3 | 14 | 21 | 7 | 4.9 | 2.7 | 9.7 |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Khaddour Case Report4 | 1 | 100 | 100 | 24+ | 24+ | 24+ |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Ferdinandus Case Report5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | 10+ |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Leven Case Report6 | 1 | 100 | 100 | 43+ | 43+ | 43+ |
|
References: 1 Shalhout et al. (2022) 2 Glutsch et al. (2022) 3 Kim et al. (2022) 4 Khaddour et al. (2020) 5 Ferdinandus et al. (2021) 6 Leven et al. (2023)
|
|||||||
| Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in the Post PD-1/PD-L1 Setting in MCC | |||||||
| Therapy | Study | N | Objective Response (%) | Complete Response (%) | Median DOR (months) | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ipilimumab +/- anti-PD1 | Hopkins/Fred Hutch Retrospective | 13 | 31 | 15 | NA | NA | NA |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | MGB Retrospective1 | 13 | 0 | 0 | NA | 1.3 | 4.7 |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | ADOREG Registry2 | 14 | 50 | 7 | NA | 5.07 | NR |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Moffitt IST No RT3 | 12 | 42 | 25 | 15.1 | 4.2 | 14.9 |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab + RT | Moffitt IST + SBRT3 | 14 | 21 | 7 | 4.9 | 2.7 | 9.7 |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Khaddour Case Report4 | 1 | 100 | 100 | 24+ | 24+ | 24+ |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Ferdinandus Case Report5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | 10+ |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Leven Case Report6 | 1 | 100 | 100 | 43+ | 43+ | 43+ |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | Aggregate | 67 | 31 | 12 | NA | NA | NA |
|
References: 1 Shalhout et al. (2022) 2 Glutsch et al. (2022) 3 Kim et al. (2022) 4 Khaddour et al. (2020) 5 Ferdinandus et al. (2021) 6 Leven et al. (2023)
|
|||||||
Of note, two patients in LoPiccolo et al. (2019) were treated with monotherapy ipilimumab and were not included in the aggregate N.
Safety
| Summary of Serious Adverse Reactions for Opdivo with Ipilimumab | ||
| Based on different diseases treatment conditions and associated trials1 | ||
| Disease Context | Trial | Serious Adverse Reactions Incidence |
|---|---|---|
| First-line Renal Cell Carcinoma | CHECKMATE-214 | 59% |
| Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma | CHECKMATE-743 | 54% |
| First-line Treatment of Unresectable Advanced or Metastatic ESCC | CHECKMATE-648 | 69% |
| First-line Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC | CHECKMATE-227 | 58% |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | CHECKMATE-040 | 59% |
| Melanoma | CHECKMATE-067 | 74% |
| MSI-H or dMMR Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | CHECKMATE-142 | 47% |
| 1 NSCLC: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, ESCC: Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | ||
Data are from the Opdivo Product Label(Bristol-Myers Squibb 2024)
Safety
| Grade 3-4 Adverse Event Percentages | ||
| Trials involving Opdivo and Ipilimumab | ||
| Disease | Trial | Grades 3-4 Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Renal Cell Carcinoma | CHECKMATE-214 | 65% |
| Melanoma | CHECKMATE-067 | 72% |
| Merkel Cell Carcinoma | MGB Retrospective | 30% |
| Merkel Cell Carcinoma | ADOREG Registry | 29% |
| Merkel Cell Carcinoma | Moffit/OSU IST | 36% |
Data are from the Opdivo Product Label(Bristol-Myers Squibb 2024), Shalhout et al. (2022), Valerie Glutsch et al. (2022) and Kim et al. (2022)
Summary
Options for patients with advanced MCC that have progressed on anti-PD1 therapy are limited
Enrollment in a clinical trial, if possible, remains the standard
Ipilimumab/nivolumab may be a reasonable options for some patients
Additional therapies with the potential for clinical benefit include cytotoxic chemotherapy and radionuclide therapy (e.g. lutetium Lu 177 dotatate)
Comfort care is also appropriate for some patients in this setting
Acknowledgements
- MGH Center for Merkel Cell Carcinoma Team
- Kevin Emerick
- Howard Kaufman
- Sonia Cohen
- Chirayu Patel
- BWH/DFCI Merkel Cell Center of Excellence Team
- Ann Silk
- Manisha Thakuria